AWS Lambda is a powerful serverless computing service that automatically runs code in response to events, without requiring you to manage the underlying infrastructure. It supports event-driven applications triggered by events such as HTTP requests, DynamoDB table updates, or state transitions.
You simply upload your code (as a .zip file or container image), and Lambda handles everything from provisioning to scaling and maintenance. It automatically scales applications based on traffic, handling server management, auto-scaling, security patching, and monitoring.

AWS Lambda is an event-driven, serverless computing platform provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It allows developers to run code in response to events while AWS automatically manages the computing resources. Lambda was first introduced in November 2014.
One of its biggest advantages is integration. You can trigger Lambda functions from over 200 AWS services, giving it strong native integrations with AWS resources. In addition, it can also connect with third-party SaaS applications, making it highly flexible.
How does AWS Lambda work?
We said that AWS Lambda fits into the event-driven architectures. So, As you can see the image AWS Lambda triggers by event and executes the function code.

Each AWS Lambda function runs inside its own container. You can think of every Lambda function as a standalone Docker-like container. When you create a function, AWS automatically packages it into a new container and executes it across a multi-region cluster of servers managed by AWS.
Resource Allocation
Before a function runs, AWS Lambda allocates the required RAM and CPU capacity. These parameters are configurable, allowing you to choose the right performance setup for your workload.
Pricing Model
The cost of Lambda depends on two factors:
- Allocated memory (RAM)
- Function execution time
The charge is calculated by multiplying memory size with execution duration. This means customers only pay for the exact resources consumed—making it highly cost-efficient.
Managed Infrastructure
The entire infrastructure behind Lambda is fully managed by AWS. Clients don’t need visibility into the underlying servers, networking, or scaling complexities. AWS handles provisioning, patching, and scaling automatically, freeing developers from infrastructure management.
Developer Benefits
By using AWS Lambda, you save significant time on operational tasks. Since there is no infrastructure to maintain, you can focus more on writing application code and building business logic. However, this convenience comes with a tradeoff—you give up some flexibility in managing infrastructure directly.
Key Features of AWS Lambda Functions
AWS Lambda offers several powerful features that make it one of the most widely used serverless computing services. Below are the core features of Lambda:
1. Auto Scaling and High Availability
AWS Lambda ensures high availability for your applications by automatically scaling them to handle sudden spikes in traffic. This guarantees uninterrupted service for end users without manual intervention.
2. Serverless Execution
There is no need to provision or manage servers manually. AWS Lambda automatically provisions the underlying infrastructure whenever a trigger event occurs. For example, if a file is uploaded to an Amazon S3 bucket, Lambda will automatically execute the function without requiring you to manage servers.
3. Pay-Per-Use Pricing
With Lambda’s pay-as-you-go pricing model, you are charged only for the compute time consumed. Billing is calculated based on the execution duration and the allocated memory size, ensuring cost savings.
4. Multi-Language Support
AWS Lambda supports a wide range of programming languages, giving developers flexibility to work with their preferred technology. Supported languages include:
- Python
- Node.js
- Java
- C#
- PowerShell
- Go
5. Integration with AWS Services
Lambda integrates seamlessly with other AWS services, enabling you to build powerful event-driven applications. Popular integrations include:
- Amazon API Gateway
- Amazon DynamoDB
- Amazon S3
- AWS Step Functions
- Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service)
- Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service)
6. Versioning and Deployment
Lambda supports versioning, allowing you to maintain multiple versions of your functions. This ensures smooth rollbacks, testing, and deployment without disrupting application performance.
7. Security and Identity Management
AWS Lambda leverages AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) to control access to your functions. You can define fine-grained permissions and policies, ensuring that only authorized users or services can invoke your Lambda functions
Steps for Creating AWS Lambda Functions Using AWS Console
- Create the Lambda Function
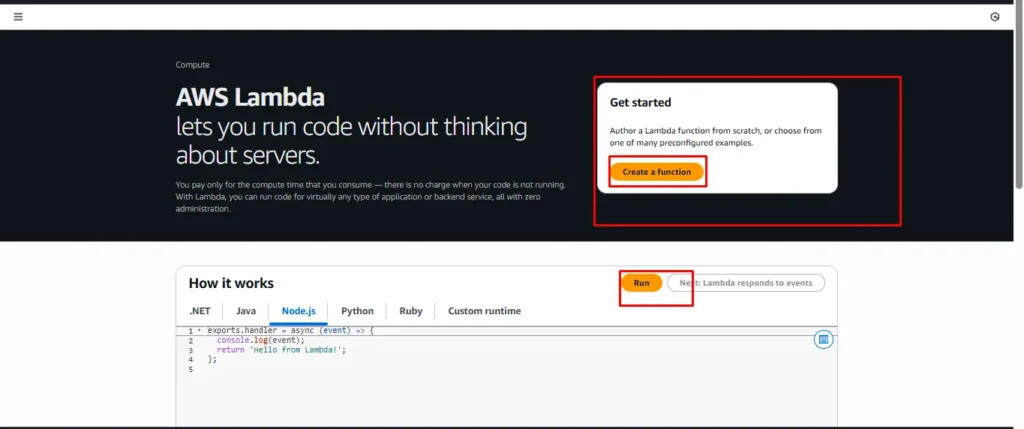
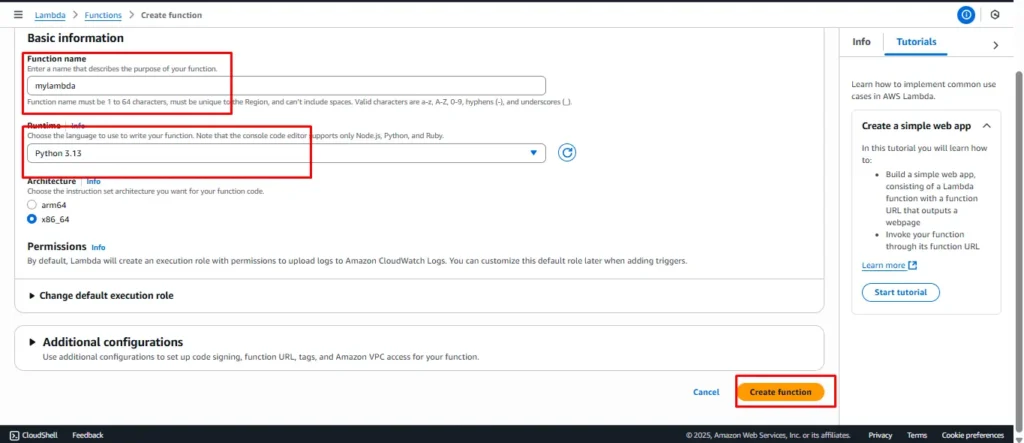
2 . Log in to AWS Console → Lambda → Create function → Choose “Author from scratch” → Enter function name → Runtime: Python 13 → Click Create.
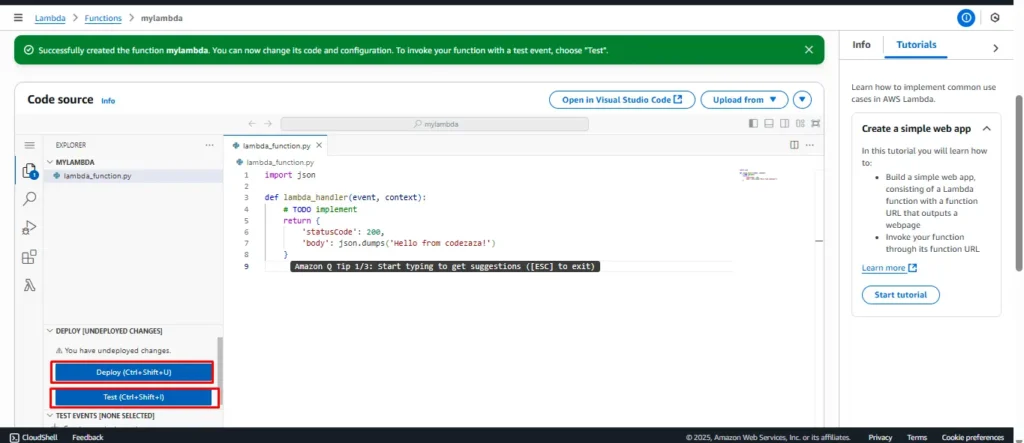
3. Write the Lambda Code
import json
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# TODO implement
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': json.dumps('Hello from codezaza!')
}
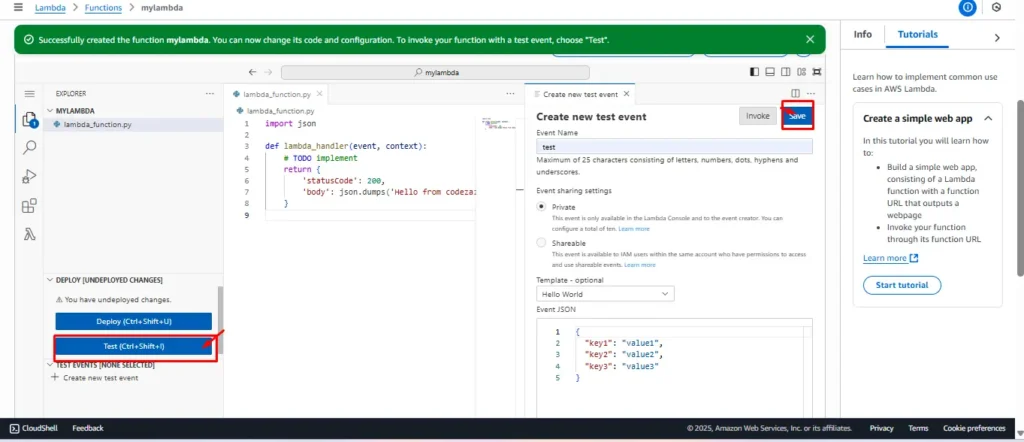
4. Configure a Test Event
In the Lambda console, click Test → Configure test event → Give it a name → Use default JSON → Save.
5. Run the Test
Click Test again → Check the execution result → Output should show statusCode: 200 and body: “Hello from Lambda!”.
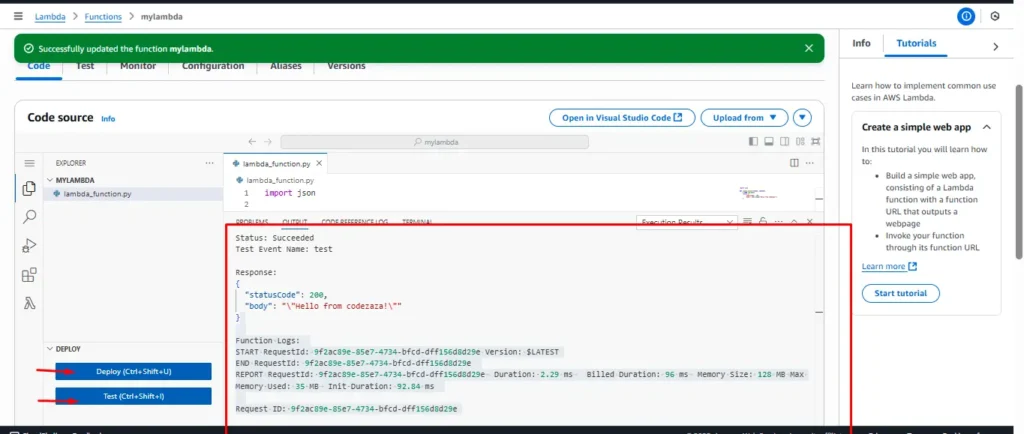
This allows you to quickly verify that your Lambda function works.
Pricing of AWS Lambda Functions
AWS Lambda pricing is based on two main factors: the number of requests to your function and the duration of code execution. With Lambda, you only pay for what you use—no upfront costs or charges for creating functions.
Each time your Lambda function starts running in response to a trigger (such as an event notification or API call), it counts as a request. The duration is measured from the moment the code begins execution until it returns a response or terminates.
If you’re unsure about whether Lambda is the right choice, AWS offers a Free Tier that includes 1 million free requests per month and 400,000 GB-seconds of compute time per month.
AWS Lambda Pricing Factors
1. Requests
AWS charges based on the total number of requests made to your function. Every request is counted individually. Pricing may vary depending on your AWS region and the total volume of monthly invocations.
2. Duration
Charges also depend on the execution duration of your function. The timer starts when your code begins running and stops once it finishes or terminates. In addition, you must allocate memory to the function, and this allocation is factored into billing.
3. Free Tier Benefits
- 1 million free requests per month
- 400,000 GB-seconds of compute time per month
These free limits apply to all users and help reduce initial costs.
Monitoring Your AWS Lambda Usage
To manage costs effectively, it’s important to monitor how your Lambda functions are being used. AWS provides native tools, and you can also integrate third-party platforms for deeper insights.
Third-Party Tools – Platforms like Datadog, Lumigo, and New Relic offer advanced monitoring, cost optimization, and performance insights.
CloudWatch Metrics – Monitor invocation counts, execution time, error rates, and memory usage. You can also set alarms when usage crosses specific thresholds.
AWS Cost Explorer – Analyze spending patterns, break down Lambda costs, and set budgets with alerts.
Usage Reports – Access detailed usage reports in the AWS Billing Console. These are useful for cost allocation across teams or multiple functions.
Conclusion
AWS Lambda is a powerful serverless compute service that allows developers to run code without managing servers or infrastructure. Its features such as auto scaling, pay-as-you-go pricing, multi-language support, and seamless AWS integrations make it one of the most flexible cloud services for modern applications.
With event-driven execution, Lambda is ideal for use cases like file processing, web applications, IoT solutions, and real-time stream processing. Its cost efficiency ensures you only pay for the resources you actually use, while its fully managed infrastructure reduces operational overhead.
Whether you are a startup looking to minimize infrastructure costs or an enterprise seeking scalable and resilient solutions, AWS Lambda provides the reliability, scalability, and performance needed to build and run applications faster.


