AWS Elastic Beanstalk is an AWS-managed service for web applications. Elastic Beanstalk is a pre-configured EC2 server that can directly take up your application code and environment configurations and use it to automatically provision and deploy the required resources within AWS to run the web application. Unlike EC2 which is Infrastructure as a service, Elastic Beanstalk is a Platform As A Service (PAAS) as it allows users to directly use a pre-configured server for their application. Of course, you can deploy applications without ever having to use elastic beanstalk but that would mean having to choose the appropriate service from the vast array of services offered by AWS, manually provisioning these AWS resources, and stitching them up together to form a complete web application. Elastic Beanstalk abstracts the underlying configuration work and allows you as a user to focus on more pressing matters.
This raises a concern that if elastic Beanstalk configures most of the resources itself and abstracts the underlying details. Can developers change the configuration if needed? The answer is Yes. Elastic Beanstalk is provided to make application deployment simpler but at no level will it restrict the developers from changing any configurations.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
As a PaaS product, Elastic Beanstalk gives developers a platform to launch and operate their apps while abstracting the underlying infrastructure. The underlying servers, networking, and other infrastructure components don’t need to be managed by developers; they may concentrate solely on writing their application code.
How Elastic Beanstalk Works
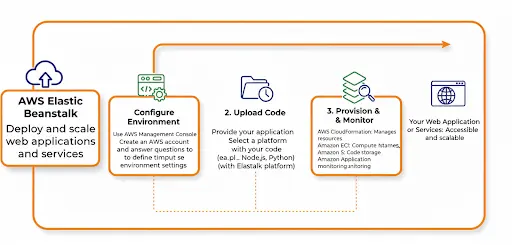
AWS Elastic Beanstalk is a managed service that simplifies cloud application deployment. It removes the need to manage servers or infrastructure. Developers create an application, pick an environment, adjust settings, and deploy their code with ease.
Elastic Beanstalk automatically provisions resources, balances traffic, scales applications, and monitors performance. This automation saves time and reduces manual effort. Teams can focus on writing code and improving features instead of managing infrastructure.
For businesses, AWS Elastic Beanstalk offers faster deployment, predictable scaling, and cost efficiency. It is an excellent choice for hosting applications in the AWS cloud.
Supported Platforms
Programming languages and platforms supported by Elastic Beanstalk include but are not limited to Java,.NET, PHP, Node.js, Python, Ruby, and Go. Additionally, it supports different application containers and web servers.
Elastic Beanstalk Features
- Elastic Beanstalk offers preconfigured runtime-like environments and deployment tools which makes it easy to deploy our application
- It supports numerous platforms and programming languages like GO, Python java, etc.
- Elastic Beanstalk scales your application automatically when the demand increases with the help of auto-scaling rules.
- Elastic Beanstalk can integrate with databases such as Mysql, Oracle, and Microsoft SQL Server.
- Access control via AWS Identity and Access Management and built-in security features like SSL/TLS encryption are provided by Elastic Beanstalk (IAM).
AWS Elastic Beanstalk Components
Application
An Elastic Beanstalk application is the container for your project code. It usually carries the same name as your project’s home directory, making it easy to identify.
Application Environments
You can run applications in different environments such as DEV, UAT, and PROD. Each environment is configurable and runs independently, helping teams manage multiple stages of development and deployment.
Environment Health
Elastic Beanstalk performs automated health checks on all EC2 deployments. These checks help ensure applications run smoothly. For example, in web apps, Elastic Beanstalk pings the service and expects a 200 status code. Health statuses include:
- Green: Application passed health checks.
- Yellow: Some checks failed.
- Red: All checks failed.
- Grey: Application is updating.
This feature allows developers to track application performance in real time from the AWS console.
Isolation
Each environment in an application is isolated from the others. Two different applications are also independent. This ensures failures or updates in one environment do not affect others.
Scalability
Elastic Beanstalk supports auto-scaling, allowing applications to handle traffic spikes dynamically without manual intervention.
Elastic Load Balancing (ELB)
Requests to your application first pass through an Elastic Load Balancer. The ELB distributes traffic across multiple instances, improving performance and reliability.
Language Support
Elastic Beanstalk supports popular programming languages such as Java, .NET, PHP, Node.js, Python, Ruby, Go, and Docker. It works with familiar servers like Apache, Nginx, Passenger, and IIS.
Pricing
There are no additional charges for Elastic Beanstalk itself. You only pay for AWS resources used, such as EC2, RDS, or S3.
Automatic Provisioning
Elastic Beanstalk automatically provisions resources and configures security groups. This removes the complexity of setting up infrastructure manually.
Impossible to Outgrow
With auto-scaling, Elastic Beanstalk can handle growing levels of internet traffic. In theory, it can scale to meet any demand without downtime
Pricing
There is no additional charge for AWS Elastic Beanstalk. You pay for AWS resources (e.g. EC2 instances or S3 buckets) you create to store and run your application. You only pay for what you use, as you use it; there are no minimum fees and no upfront commitments.
The costs of running a web site using Elastic Beanstalk can vary based on several factors such as the number of Amazon EC2 instances needed to handle your web site traffic, the bandwidth consumed by your application, and which database or storage options your application uses. The principal costs for a web application will typically be for the Amazon EC2 instance(s) and for the Elastic Load Balancing that distributes traffic between the instances running your application.
Conclusion
AWS Elastic Beanstalk is a powerful Platform as a Service (PaaS) that streamlines the deployment and management of web applications in the AWS cloud. By abstracting the underlying infrastructure, it allows developers to focus entirely on writing and improving application code rather than managing servers, networking, or storage. With features like automatic provisioning, auto-scaling, Elastic Load Balancing, integrated security, and support for multiple programming languages and frameworks, Elastic Beanstalk simplifies the end-to-end deployment process while providing flexibility for configuration changes.
Elastic Beanstalk also offers robust environment management, including health monitoring, isolation between environments, and seamless scalability, making it suitable for applications of any size. Its cost model is straightforward, as there are no additional charges beyond the AWS resources consumed, ensuring predictable and efficient use of cloud resources. Overall, Elastic Beanstalk enables faster deployment, operational simplicity, and reliable performance, making it an ideal choice for businesses and developers looking to build, scale, and maintain cloud applications efficiently.


