AWS CodeCommit is a fully managed source control service from Amazon Web Services (AWS). It helps developers store and manage code, documents, and even binary files in a secure cloud environment. Unlike traditional systems, CodeCommit removes the need for your own infrastructure or third-party version control tools.
You can use it with your existing Git tools and perform operations like push, pull, and commit without extra setup. Teams can collaborate easily while relying on AWS’s scalability and security. Creating repositories takes just a few clicks, and you can manage code or share projects across AWS accounts in a secure way.
CodeCommit also supports cross-account access, but you must avoid sharing SSH keys or AWS credentials to keep the environment safe. By using this service, organizations simplify code management, improve security, and boost developer productivity.
Git Vs AWS CodeCommit

Differences
- AWS CodeCommit is more secure than the git as AWS uses IAM roles for securing techniques which allows users to share their repositories to the limited person and in highly secure environment.
- Git interface comes out to be more interactive than the AWS CodeCommit .
- Git is basically connected to the github whereas AWS CodeCommit is managed and hosted by the AWS which is more reliable platform.
Similarities
- Both can integrate with AWS cloudbuild that can import your github and other Google cloud storage to your specifications and produce containers.
- Both uses git repositories.
- Both supports code review.
Steps for creating a repository in CodeCommit
Step 1: Login to your AWS account and navigate to the Amazon Management console. In the search bar search for the AWS CodeCommit . A CodeCommit service window will appear.
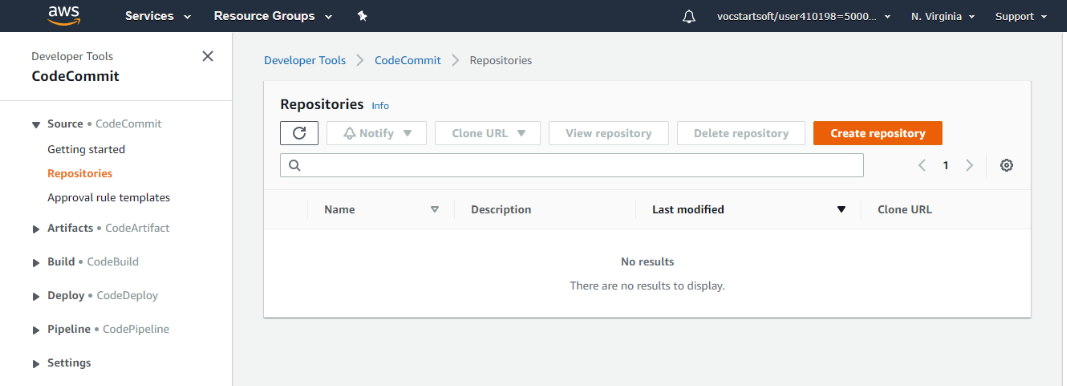
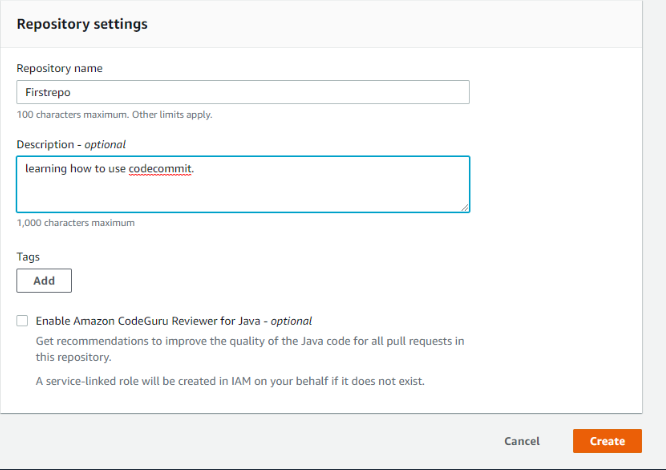
Step 2: Click on create repository to create the repository in aws CodeCommit . Type a name and add a description of it and then click on create.
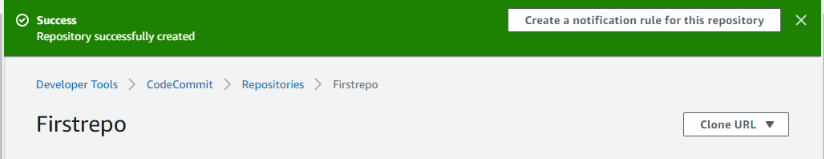
Step 3: A success message will appear on the screen showing successful creation of repository.
Step 4: There are two ways to connect your repository HTTP and SSH. In this we are using HTTP. Click on create file to add your file.
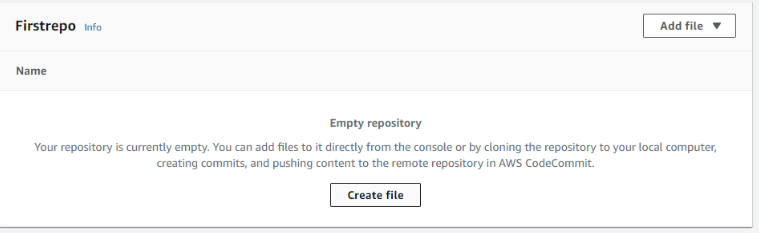
Step 5: In this we are typing a text file.you can store your source code or any other binary files.
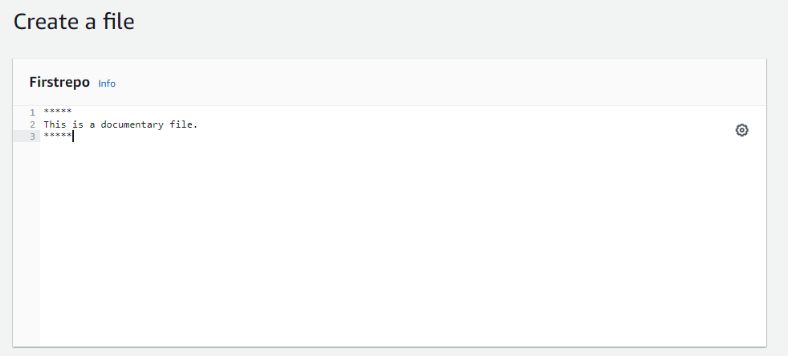
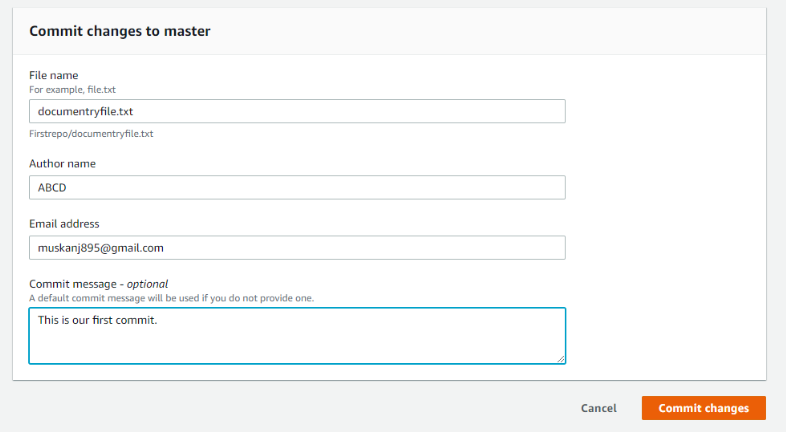
Step 6: Add Filename, Author name, Email ID, Commit message and click on Commit Changes.
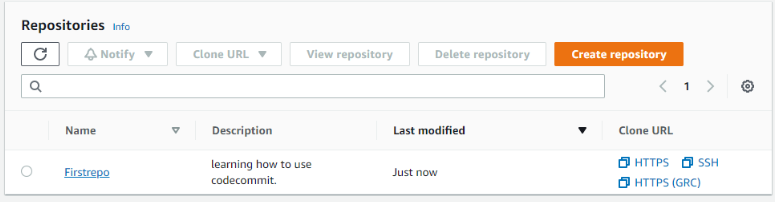
- Step 7: This is how you can create your repository easily within few clicks.
Benefits of Using AWS CodeCommit
1. Highly Scalable
AWS CodeCommit scales up or down based on your data needs. It can manage large repositories and multiple branches without performance issues.
2. Fully Managed
As a developer, you can focus on building applications instead of managing hardware or software. CodeCommit handles infrastructure, availability, and durability for you.
3. Easy Collaboration
Multiple users can work on the same source code at the same time. Changes and updates are merged and pushed into the repository with ease.
4. Strong Security
CodeCommit provides a secure environment for source code, documents, and binary files. It uses encryption and IAM roles to protect your data and control access.
5. Simple Migration
You can migrate existing Git repositories to CodeCommit quickly. This makes it easier to adopt AWS without changing your development workflow.
Integrating AWS CodeCommit with Other Tools and Services
AWS CodeCommit integrates with many tools and services to create a seamless workflow for developers. For example, you can connect CodeCommit with AWS CodePipeline to automate the build, test, and deployment process. This reduces the time and effort needed to release new features and updates.
In addition, CodeCommit works smoothly with Git. You can migrate an existing codebase to AWS CodeCommit or continue using your current Git tools. At the same time, you gain the scalability and security of AWS.
Moreover, AWS CodeCommit integrates with services like AWS CodeBuild, AWS CodeDeploy, and AWS CodeStar. Together, they enable a complete end-to-end workflow for developing, building, and deploying applications on AWS. By leveraging these integrations, you can streamline development, speed up delivery, and take full advantage of the AWS ecosystem.
Conclusion
Using AWS CodeCommit for source control provides a secure, scalable Git repository to empower your development team. We covered the end-to-end process from creating a CodeCommit repository to connecting it locally and utilizing Git commands to update code changes. Key highlights include initializing a repository with useful documentation for other developers, setting up efficient authentication methods like SSH or HTTPS, leveraging Git workflows to stage, commit and push updates, and managing fine-grained user permissions with IAM. Following these best practices for using CodeCommit and Git collaboration enables continuous integration for making seamless code changes. The AWS management console streamlines creating and maintaining repositories while Git facilitates local workflows. Together, they provide version control with the flexibility to customize access based on your team needs. As you progress in leveraging CodeCommit, consider integrating triggers for automation and utilizing CloudTrail logs for auditing. AWS offers robust tools for organizations to implement DevOps around hosting and updating source code. By mastering CodeCommit fundamentals, you can establish scalable workflows to manage projects as they grow in complexity.


