Amazon Web Services(AWS) offers cloud formation as a service by which you can provision and manage complicated services offered by AWS by using the code. CloudFormation will help you to manage the infrastructure and the services in the form of a declarative way.
AWS CloudFormation is an Infrastructure as Code (IaC) offering that allows you to describe and provision AWS infrastructure in a repeatable and automated way. You write CloudFormation templates (in JSON or YAML) to specify the resources you require, like EC2 instances, S3 buckets, or RDS databases, and CloudFormation does the work of creating, managing, and updating them for you.
With CloudFormation, you can treat your infrastructure as one unit, known as a stack, to be able to easily replicate and have consistency between various AWS environments and regions. This eliminates the requirement for manual configuration, which is prone to errors and takes time.
How Does AWS CloudFormation Work?
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is the service offered by the AWS cloud it is mainly used to provision the service in the AWS like EC2, S3, Autoscaling, load balancing and so on you can provision all the service automation with the Infrastructure as a code (IAC), instead of managing all of them manually you can manage with the help of AWS Cloudformation.

Features Of AWS CloudFormation
1. No Upfront Investment
AWS CloudFormation operates on a pay-as-you-go model, meaning there is no need for large upfront costs.
2. Lower Operating Costs
By automating infrastructure provisioning, CloudFormation helps reduce the time and resources needed for manual management, lowering operational expenses.
3. Highly Scalable
Easily scale your infrastructure up or down according to your needs without the hassle of manual intervention.
4. Easy Access
CloudFormation is integrated with the AWS Management Console, providing users with an intuitive interface to manage resources.
5. Reduces Business Risks and Maintenance Expenses
Automation through CloudFormation ensures consistency across environments, reducing human error and the cost of maintenance.
Use Cases Of AWS CloudFormation
1. Infrastructure Provisioning
You can automate provisioning of complex infrastructures in various environments using CloudFormation. Defining your infrastructure in code helps you to duplicate your infrastructure identically in other regions using one template.
2. Auto-Scaling Environments
You can create auto-scaling groups using CloudFormation so that your resources scale automatically depending on load, with optimal performance and cost.
3. Multi-Region Deployments
With CloudFormation, you can provision resources in multiple regions so that your infrastructure is disaster-resistant or resistant to a failure in a particular region.
4. CI/CD Pipeline Integration
CloudFormation supports integration with AWS Code Pipeline, Jenkins, and other CI/CD tools so that you can automate the deployment of infrastructure as well as application code.
Benefits of AWS CloudFormation
1. Automation
AWS CloudFormation helps to automate the process of creating, configuring, and managing AWS resources. This allows for the infrastructure to be deployed quickly, reliably, and repeatedly.
2. Consistency and standardization
With AWS CloudFormation, it is possible to create standard templates of infrastructure stacks that can be used to create identical copies of the same infrastructure. This ensures consistency in the infrastructure deployment and makes it easier to maintain.
3. Cost savings
AWS CloudFormation helps to reduce costs by allowing customers to use existing infrastructure templates and reuse them across multiple environments. This reduces the cost of designing and deploying new infrastructure.
4. Security
AWS CloudFormation helps to ensure that all AWS resources are configured securely by using security policies and rules. This helps to protect the infrastructure from potential security threats.
5. Scalability
AWS CloudFormation allows for the quick and easy scaling of resources on demand. This means that customers can quickly and easily add resources to meet their changing needs.
Amazon Web Services is a subsidiary of Amazon.com that provides on-demand cloud computing platforms to individuals, companies, and governments, on a paid subscription basis.
Why Do We Need AWS CloudFormation?
Just imagine that you have to develop an application that uses various AWS resources. When it comes to creating and managing those resources, it can be highly time-consuming and challenging. It can become difficult for you to develop the application when you are spending the whole time managing those AWS resources. What if we have a service for that? So here comes AWS Cloudformation in the picture.
Getting Started with AWS CloudFormation
When you begin with AWS CloudFormation, you need a template that defines your infrastructure. This template can be written in JSON or YAML. In this article, we will focus on the JSON format.
JSON is a text-based format that uses JavaScript object syntax to represent structured data. With CloudFormation, the JSON script describes all the AWS resources you want to create. Based on this structure, CloudFormation automatically provisions and manages your infrastructure.
By using JSON templates, you can:
- Clearly define your AWS resources in a single file.
- Deploy infrastructure consistently across environments.
- Save time by automating resource creation.
In short, JSON scripts act as the blueprint for your cloud environment, making CloudFormation a powerful tool for Infrastructure as Code (IaC).
Structure of a CloudFormation JSON Template
A CloudFormation JSON template is made up of different sections. Each section has a specific role in defining your AWS infrastructure. Let’s go through them one by one:
- Format Version: This defines the version of the template. It helps CloudFormation understand which features the template supports.
- Description: Here, you can add comments or details about your template. This makes it easier for others (and your future self) to understand its purpose.
- Metadata: Use metadata to provide extra information in the form of JSON objects. For example, you can add details about resources or configuration settings.
- Parameters: Parameters allow you to pass custom values to the stack during runtime. With them, you can create flexible and reusable templates.
- Mappings: Mappings let you define key-value pairs. They are useful when you need to choose values based on conditions, such as region or environment.
- Conditions: With conditions, you can decide whether to create certain resources or assign values to properties. This makes your template smarter and more dynamic.
- Transform: The transform section lets you reuse components. For instance, you can simplify your template using AWS::Include or the AWS SAM transform.
- Resources: This is the most important section. Here, you define the AWS resources you want, such as EC2 instances, S3 buckets, or Lambda functions.
- Outputs: Finally, outputs provide useful information after stack creation. For example, you can output the DNS name of a load balancer or the ARN of a resource.
CloudFormation Template Terms and Concepts
Understanding The Core Concepts That CloudFormation templates use to organize resources, settings, and functions is key to managing AWS infrastructure efficiently.
1. Template
A CloudFormation template is a simply JSON or YAML file that defines the AWS resources to be created and configured.
2. Stacks
Stacks are the totality of the resources which are contained within a CloudFormation Template. When one wishes to roll out a template , they will be required to roll out a stack in which all the available resources in that stack will be rolled out as one.
3. Formatting
JSON and YAML is used in handling templates within CloudFormation. YAML has been very much opted for in terms of using due to forthcoming advantages in smaller templates and large templates as well.
4. Change Sets
Change sets are used to examine what CloudFormation will do, in terms of modification or change , to the deployed resources when an update operation is required on a specific stack. It ensures that all the changes that are executed on the infrastructure do not create risks that were not intended.
5. Functions
CloudFormation comes with several built-in functions (like Fn::Sub, Fn::Join), and these functions are aimed at making dynamic configuration easier so that as the resources are being deployed, their properties can be adjusted and modified.
6. Parameters
These offer an opportunity for user interaction during the deployment of the stack thus making it easier to create templates that are flexible and reusable. For instance, given the instance types, VPC ids or environment variables can be indicated as parameters.
7. Conditions
Conditions enable or disable the creation of a resource depending on whether certain conditions are true or false (for example, it may depend on the environments of production or development). This allows for more complex template logic, deploying different resources based on provided parameters.
How to Deploy a CloudFormation Template
Deploying a CloudFormation template can be done through multiple methods, each catering to different preferences and workflows
1. AWS Management Console
The AWS Management Console offers a user-friendly way to deploy templates. Simply log in, navigate to CloudFormation, and select “Create Stack.” You can then upload your template (in JSON or YAML format), configure parameters, tags, and permissions, and finalize by clicking “Create Stack.” This method is ideal for those who prefer a visual, straightforward interface.
2. CloudFormation Designer
For a more graphical approach, CloudFormation Designer allows users to visually build or modify templates using a drag-and-drop interface within the AWS Console. After creating or adjusting your template, deployment is just a click away by selecting “Create Stack.” This method suits users who enjoy visual tools for infrastructure design.
3. AWS CLI (Command Line Interface)
After ensuring the AWS CLI is installed and configured, you can deploy your template by running a simple command. This method is particularly useful for developers who want to integrate deployments into CI/CD pipelines or automate infrastructure tasks.
What Are AWS CloudFormation Hooks?
AWS CloudFormation Hooks is a powerful feature that helps ensure your CloudFormation resources comply with your organization’s security, operational, and cost optimization standards. CloudFormation Hooks allows you to implement custom code that proactively checks the configuration of AWS resources before they are provisioned. If any resources are found to be non-compliant, CloudFormation can either block the provisioning process or issue a warning while allowing the process to continue, providing enhanced control over your infrastructure setup.
Benefits of Using CloudFormation Hooks
Benefits of Using CloudFormation Hooks
1. Automatic Compliance Checking
CloudFormation Hooks automatically verify that your resources meet your organization’s rules and standards before deployment. By catching non-compliant resources early, it helps prevent issues and ensures that only resources compliant with your policies are provisioned in your cloud environment.
2. Personalized Checks
You have the flexibility to create custom checks tailored to your specific organizational needs. These checks ensure resources adhere to your defined standards before they are deployed, giving you full control over your cloud infrastructure.
3. Manage Resource Lifecycles
CloudFormation Hooks allows you to track and manage resources throughout their lifecycle, ensuring they remain compliant with your rules and standards from provisioning to decommissioning.
4. Cost Optimization
By enforcing guidelines that control resource usage, CloudFormation Hooks helps prevent unnecessary spending and ensures cost-efficient infrastructure management. You can set rules to limit the over-provisioning of resources, effectively controlling costs and optimizing spending.
5. Enhanced Security
CloudFormation Hooks adds an extra layer of security by enforcing strict security policies during resource provisioning. This ensures that unauthorized or risky configurations are prevented, thereby enhancing the overall protection of your cloud environment.
How to Create an AWS CloudFormation Template
There are two main ways to create an AWS CloudFormation template:
1. Use Pre-Built Templates
You have two options when using a pre-built template:
- Choose an Existing Template: You can select a previously created template and customize it to fit your needs. This option allows you to modify the template to suit your current requirements.
- Use a Sample Template: AWS provides several sample templates to help you get started. You can choose one of these sample templates and modify it to deploy your infrastructure. This article uses this approach. Once you select a sample template, you can customize it to match your infrastructure setup.
2. Build Your Own Template from Scratch
If you prefer a more hands-on approach, you can use AWS Application Composer to visually design your template. This tool offers a drag-and-drop interface, making it easier to c onfigure infrastructure components without needing to write code. It’s a great choice if you want to build a template visually and generate it automatically.
Steps to Provision an EC2 Instance Using AWS CloudFormation
Step 1: Log in to the AWS Console
Begin by signing in to the AWS Management Console.
After that, navigate to the CloudFormation service from the dashboard.
Step 2: Create a New Stack
Click Create stack → With new resources (standard).
Next, choose Template is ready to move ahead.
Under Specify template, you can:
- Upload a JSON/YAML file directly, or
- Provide an Amazon S3 URL if your template is stored in S3.
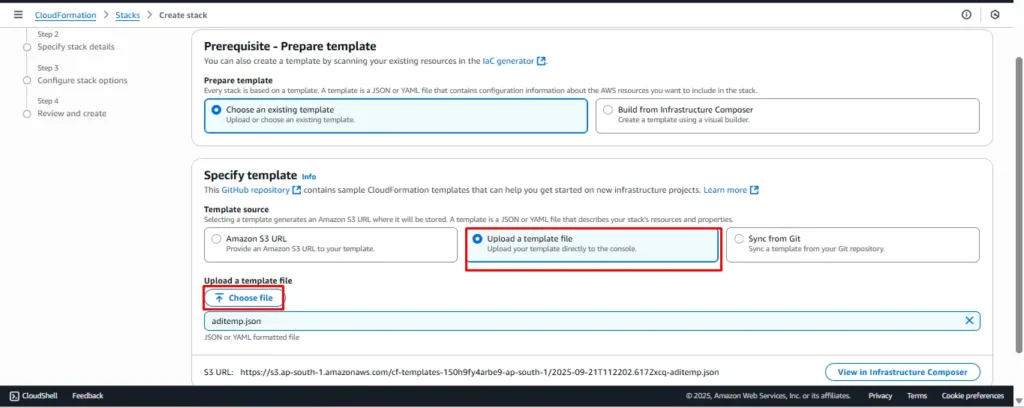
Step 3: Use a Sample CloudFormation Template (JSON)
Here’s a simple JSON template that provisions a t2.micro EC2 instance in the default VPC:
{
"AWSTemplateFormatVersion": "2010-09-09",
"Description": "CloudFormation template to launch an EC2 instance",
"Resources": {
"MyEC2Instance": {
"Type": "AWS::EC2::Instance",
"Properties": {
"ImageId": "ami-0c55b159cbfafe1f0",
"InstanceType": "t2.micro",
"KeyName": "my-keypair",
"SecurityGroups": ["default"]
}
}
},
"Outputs": {
"InstanceId": {
"Description": "The Instance ID",
"Value": { "Ref": "MyEC2Instance" }
},
"PublicIP": {
"Description": "The Public IP address of the instance",
"Value": { "Fn::GetAtt": ["MyEC2Instance", "PublicIp"] }
}
}
}
- Replace
"ami-0c55b159cbfafe1f0"with a valid AMI ID for your AWS region. - Update
"my-keypair"with your actual EC2 key pair name.
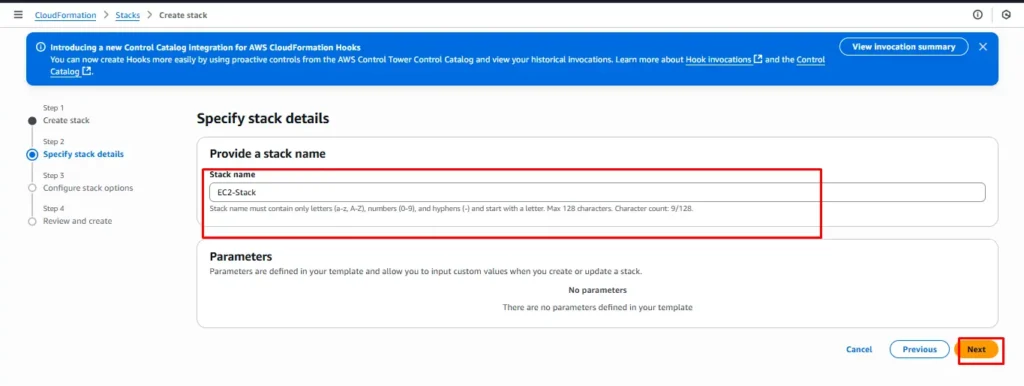
Step 4: Configure Stack Settings
Provide a Stack Name, such as EC2-Stack.
Then, fill in the required parameters like the key pair name.
Once done, click Next to continue.
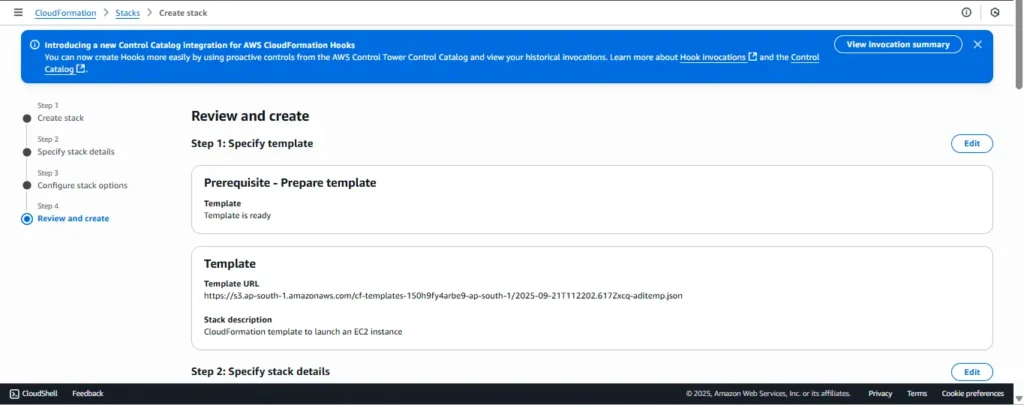
Step 5: Review and Create
At this stage, carefully review the template details.
If CloudFormation asks for additional permissions, grant them so it can create IAM resources.
Finally, hit Create stack to deploy the EC2 instance.
Step 6: Monitor the Stack
Head over to the CloudFormation Stacks page to track the deployment progress.
The status will eventually change to CREATE_COMPLETE.
When it does, open the Outputs tab to view the Instance ID and Public IP.
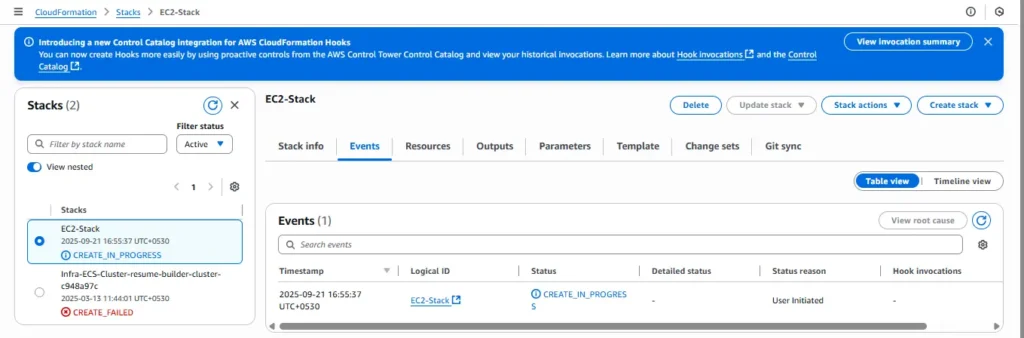
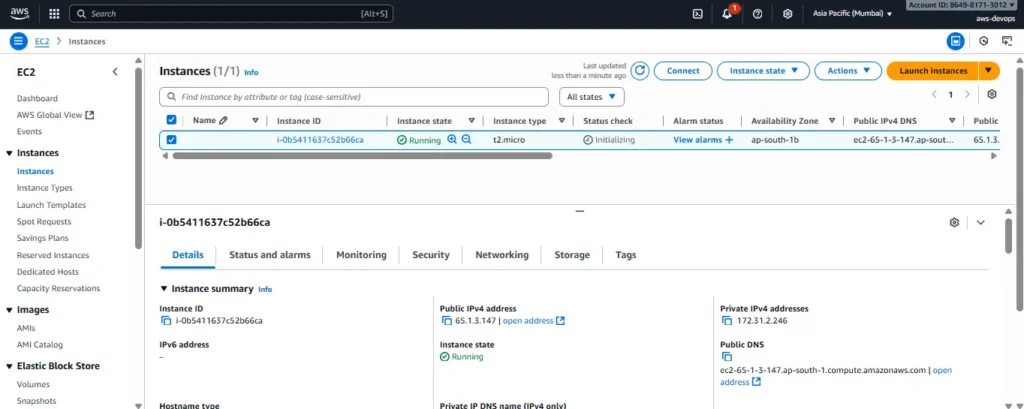
Step 7: Verify the EC2 Instance
Switch to the EC2 Dashboard from the AWS Console.
Here, confirm that your instance is up and running successfully.
Alternatives to CloudFormation
AWS CloudFormation is a very Famous infrastructure-as-code tool for managing AWS resources several alternatives offer different features and support for multi-cloud environments. Listing out some of very popular alternatives.
- Terraform: Terraform is an open-source infrastructure-as-code tool where It Allows you to Implement CI/CD Pipeline By integrating Multiple cloud providers like Azure ,Google cloud and more
- Pulumi: Pulumi Is a Power-full Infrastructure-as-code tool That Allows you To Automate and provision your Resources .It supports various cloud platforms Like AWS, Azure, OCI and More Cloud Provider
Difference Between AWS CloudFormation and Terraform
Both AWS CloudFormation and Terraform are popular Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools. However, they differ in scope, features, and flexibility. Let’s compare them across key parameters:
| S.No | Parameter | CloudFormation | Terraform |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Multi-Cloud Support | Works only with AWS services, as it is AWS-specific. | Supports multiple cloud providers, so it is more versatile in multi-cloud setups. |
| 2 | Language | Uses JSON or YAML to define templates. | Uses HCL (HashiCorp Configuration Language) or JSON, designed for human readability. |
| 3 | Community and Ecosystem | Has strong integration with AWS and an AWS-focused community. | Has a larger and more diverse community because it supports many providers. |
| 4 | State Management | AWS handles state management automatically. | Requires explicit state management, but you can store the state remotely for collaboration. |
| 5 | Drift Detection | Provides stack drift detection to highlight changes in the actual infrastructure. | The terraform plan command shows changes before applying, helping detect drift. |
| 6 | Failure Handling | Can roll back changes automatically when errors occur. | Requires you to fix the issue and retry the deployment. |
Conclusion
AWS CloudFormation is a tool that allows you to automate and manage AWS resources using code. With CloudFormation, you can define your infrastructure in JSON or YAML templates, making it easy to create, update, and replicate resources without manual intervention. This approach helps reduce errors, save time, and ensure consistency across different environments.
By automating tasks like scaling resources, multi-region deployments, and integrating with CI/CD pipelines, CloudFormation makes cloud management simpler and more efficient. It also helps lower costs and enhance security by ensuring all resources meet your organization’s standards.
Overall, AWS CloudFormation is a powerful tool for businesses that want to easily manage their cloud infrastructure, improve efficiency, and focus more on growing their applications rather than managing resources manually.


