AWS Virtual Private Network (AWS VPN) creates a secure and private tunnel between your network or device and the AWS Cloud. You can connect to additional AWS resources from a client or expand your current on-premises network into a VPC.
What is Virtual Private Network?
VPN (Virtual Private Network) refers to the ability to establish a secure network connection when using public networks. VPNs mask your online identity and encrypt your internet activity. This makes it more challenging for outside parties to monitor your internet activities and steal data. Real-time encryption is employed.
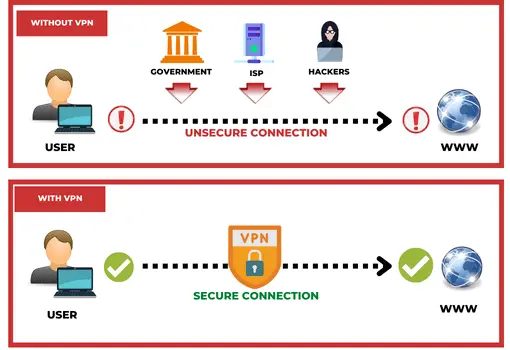
What is AWS VPN?
AWS Virtual Private Network (VPN) solutions connect your on-premises networks, distant offices, client devices, and the AWS global network in a secure manner. AWS Client VPN and AWS Site-to-Site VPN are the two services that make up this system. Each service offers a managed, scalable, and highly available cloud VPN solution to secure your network traffic.
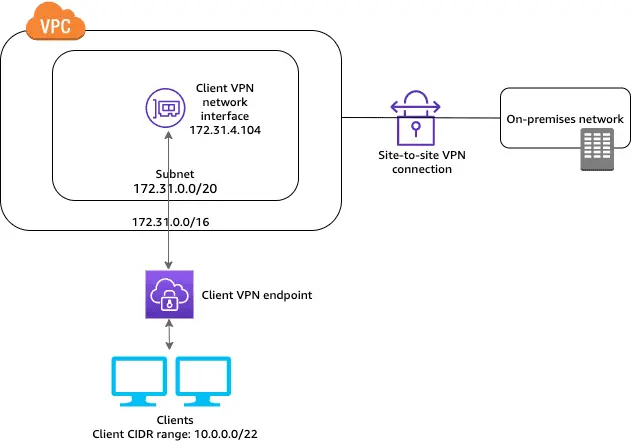
Components of AWS VPN
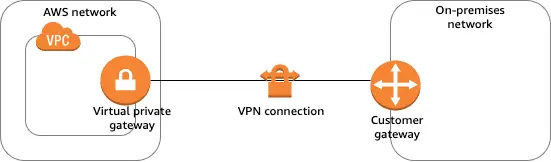
Virtual Private Gateway (VGW):
A Virtual Private Gateway is the AWS-managed VPN concentrator that sits on the Amazon side of the connection. It serves as the anchor point in your Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). Through this gateway, you can create secure IPsec tunnels between AWS and your on-premises or cloud networks. Moreover, the VGW is designed to be highly available and scalable, so it can support multiple VPN connections at the same time. In addition, it automatically handles failover between tunnels to ensure constant connectivity. As a result, it provides a reliable and secure path for both inbound and outbound traffic, keeping all communication encrypted.
Customer Gateway (CGW):
A Customer Gateway is a physical device or software application located at your premises. It connects directly to the AWS Virtual Private Gateway and represents your side of the VPN connection. The CGW is responsible for creating and maintaining the IPsec tunnels to AWS. It can be a hardware router, firewall device (for example, Cisco or Juniper), or even a software VPN running on a server. To work properly, the CGW must be configured with routing rules, encryption algorithms, and authentication settings that align with the VGW. Consequently, when combined, the CGW and VGW establish a secure site-to-site VPN. This setup allows seamless and encrypted communication between your on-premises infrastructure and AWS resources.
Types of AWS VPN
It provides two private connectivity options with the high availability and strong security your data needs:

AWS Client VPN:
It is a fully managed remote access VPN solution that allows your distant employees to safely access resources on AWS as well as your on-premises network. It automatically adjusts up or down dependent on demand because it is fully elastic. Your users can access your applications in the same way before, during, and after the transfer to AWS.
The OpenVPN protocol is supported by AWS Client VPN, including the software client.
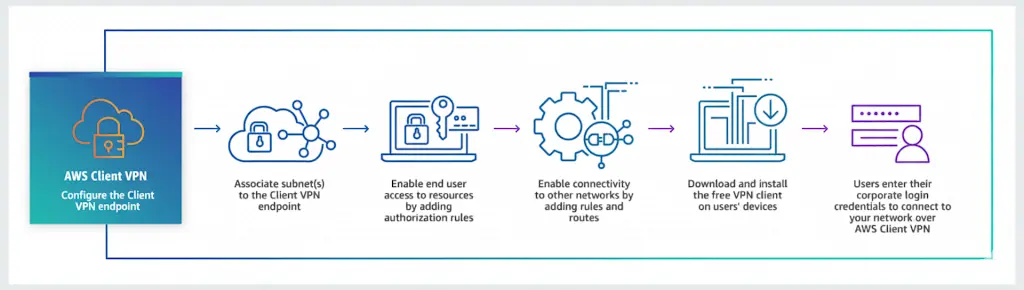
How it works
Use Cases:
- Quickly scale remote access: Many of your employees could have to work remotely due to unforeseen circumstances. Due to the increase in VPN connections and traffic, your users’ experience may suffer in terms of performance or availability.
- Access applications during migration: Users can securely access applications both on-premises and on AWS thanks to AWS Client VPN. This is useful when moving apps from on-premises sites to the cloud during a cloud migration.
- Integrate with your authentication and MDM systems: When utilising the AWS-provided OpenVPN Client software, AWS Client VPN enables authentication using Microsoft Active Directory using AWS Directory Services, Certificate-based authentication, and Federated Authentication using SAML-2.0.
- Securely connecting IoT devices: Utilizing certificate-based authentication, establish secure connections between IoT devices and Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) resources.
Features:
- Authentication: Either Active Directory or certificates will be used for authentication. It works with AWS Directory Services, which links to your existing on-premises Active Directory, thus it does not require you to duplicate data from your existing Active Directory to the cloud.
- Authorization: It offers network-based authorization, allowing you to create access control rules based on Active Directory groups that restrict access to particular networks.
- Secure connectivity: It encrypts the traffic using the safe TLS VPN tunnel protocol. Each Client VPN endpoint terminates a separate VPN tunnel that gives users access to both on-premises and AWS services.
- Connection management: Amazon CloudWatch Logs can be used to monitor, store, and access log files from AWS Client VPN connection logs. The associated log data can then be obtained from CloudWatch Logs.
- Compatibility with your employees’ devices: Devices can be connected to your network using it. Employees have the flexibility to utilize any device they like, including Windows, Mac, iOS, Android, and Linux-based devices, thanks to its selection of OpenVPN-based clients.
Pricing
AWS Client VPN charges you based on two factors. First, you pay for the number of active client connections per hour. Second, you pay for the number of linked subnets per hour. This pay-as-you-go model ensures you only pay for what you use.
Best Practices for AWS Client VPN
- Use strong authentication methods
Always integrate Client VPN with AWS Directory Service, Active Directory, or a SAML-based identity provider. This ensures secure user authentication. - Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Add MFA to increase security. Even if a password is compromised, MFA prevents unauthorized access. - Follow the principle of least privilege
Restrict users to only the networks and resources they need. Use authorization rules to limit access. - Enable split tunneling when possible
Split tunneling reduces bandwidth costs by sending only AWS-related traffic through the VPN. Other traffic goes directly to the internet. - Monitor and log connections
Use Amazon CloudWatch and AWS CloudTrail to track client activity. Regular monitoring helps detect unusual patterns. - Use encryption best practices
Configure strong encryption algorithms for the VPN tunnels. This protects data in transit from interception. - Scale connections properly
Plan capacity for peak usage. AWS Client VPN scales automatically, but monitoring helps ensure smooth performance. - Regularly review subnet associations
Check which subnets you link to the VPN. Remove unused associations to reduce costs and security risks.
AWS Site-to-Site VPN
AWS Site-to-Site VPN is a fully managed service that uses IP Security (IPSec) tunnels to create a secure link between your data center or branch office and AWS resources. You can connect to both Amazon Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) and the AWS Transit Gateway. Each connection includes two tunnels, which increase redundancy and reliability.
The Accelerated Site-to-Site VPN option works with AWS Global Accelerator. It dynamically routes your traffic to the nearest AWS network endpoint. As a result, it improves speed and delivers better performance for applications that run across multiple regions.
How it works
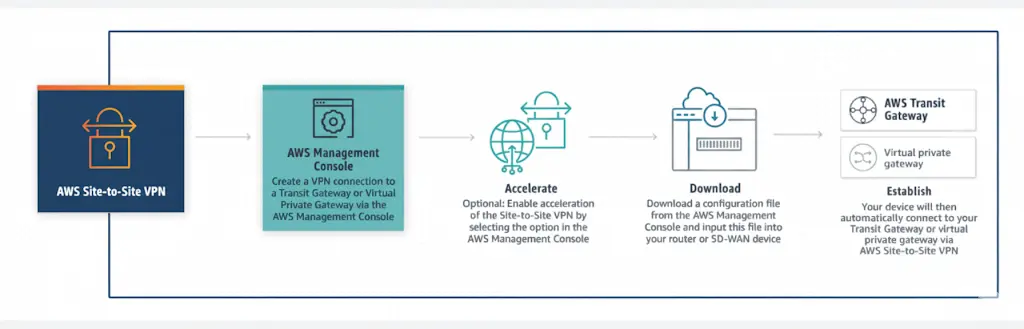
Use Cases:
- Application Migration: A Site-to-site VPN connection between your network and the AWS cloud makes moving applications to the cloud easier. You can host Amazon VPCs behind your corporate firewall and migrate your IT resources without disrupting your users’ access to these applications.
- Secure communication between remote locations: AWS Site-to-Site VPN connections can be used to securely communicate between remote sites.
Features:
- Secure connectivity: It employs OpenVPN, which negotiates data channel parameters over a TLS encrypted control channel.
- High availability: With AWS Direct Connect, you can create failover and CloudHub solutions. CloudHub allows your remote sites to communicate with one another as well as with the VPC.
- Customization: It provides tunnel customization options such as inside tunnel IP address, pre-shared key, and Border Gateway Protocol Autonomous System Number (BGP ASN).
- Network Address Translation (NAT) Traversal: It supports NAT Traversal applications, allowing you to use private IP addresses behind routers on private networks with a single public IP address facing the internet.
- Private IP VPN: Private IP VPN enables the use of private IP addresses to deploy site-to-site VPN connections over Direct Connect (DX).
- Monitoring: It can send metrics to CloudWatch to improve visibility and monitoring. CloudWatch also lets you send your own custom metrics and add data points in any order and rate you want.
Pricing
You are charged for each VPN connection hour that your VPN connection is provisioned and available if you create an AWS Site-to-Site VPN connection to your Amazon VPC. Each hour of partial VPN connection consumption is billed as a full hour. All data transferred via the VPN connection is also subject to standard AWS data transfer charges.
Best Practices of AWS Site-to-Site Connection
The following are the best practices of AWS Site-to-Site Connection:
- Use Redundant Connections: On setting up the multiple VPN tunnels, we can ensure high availability and failover protection.
- Regularly Monitor and Maintain: By using the AWS CloudWatch we can monitor the VPN’s health and performance, and promptly address any issues.
- Implement Strong Encryption: It helps in ensuring that the data is encrypted using robust encryption algorithms and regularly update your security configurations.
- Keep Security Groups Updated: It helps in regularly review and update security group rules to allow only necessary traffic and minimize exposure.
AWS Direct Connect vs AWS Site-to-Site VPN
Vs Client-to-Client-VPN
| Feature | AWS Direct Connect | AWS Site-to-Site VPN | AWS Client VPN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Connection Type | Provides a dedicated private network connection between on-premises and AWS | Establishes an encrypted IPsec tunnel over the public internet | Uses an OpenVPN-based client to connect individual users securely to AWS |
| Performance | Delivers high performance with consistent, low latency | Offers variable performance because it depends on the internet | Provides scalable performance for many users, but depends on internet quality |
| Security | Ensures a private and secure connection without internet exposure | Provides secure communication using encryption over the internet | Uses strong authentication, MFA, and encryption to secure remote user access |
| Cost | Higher cost due to dedicated infrastructure | Lower cost because it uses existing internet infrastructure | Pay-as-you-go pricing based on active connections and linked subnets |
| Use Case | Best for consistent, high-throughput, latency-sensitive workloads | Suitable for flexible, lower-cost, site-to-site connectivity | Ideal for remote employees, contractors, or developers needing secure access |
Conclusion
AWS offers multiple VPN solutions to meet different connectivity needs. Site-to-Site VPN provides secure, encrypted tunnels between on-premises networks and AWS resources, while Client VPN enables remote users to connect safely from anywhere. For organizations that need consistent, high-throughput connections, Direct Connect offers a private and dedicated link. By choosing the right VPN option based on performance, cost, and security requirements, businesses can build a reliable and flexible hybrid networking strategy on AWS.


