Deploying applications reliably and efficiently in Kubernetes requires automation, scalability, and minimal downtime. In this guide, we demonstrate an end-to-end deployment using Argo CD with Helm, implementing a rolling update strategy and Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA). You’ll learn how to structure your Helm charts, integrate with GitHub for continuous delivery, and leverage Argo CD’s powerful UI to manage deployments. By the end, your application will be capable of seamless updates with zero downtime and easy rollbacks, ensuring robust production-ready operations.
Project Structure
├── calori-chart/ # Helm Chart directory
│ ├── templates/
│ │ └── deployment.yaml # Contains rolling update strategy
│ ├── values.yaml # Image, replicaCount, ports
│ └── Chart.yaml
├── Dockerfile
├── Jenkinsfile
├── Deployment.yaml # Optional: base deployment for reference
├── service.yaml
└── README.md
Prerequisites
- Kubernetes Cluster (e.g., Minikube, EKS, etc.)
- Argo CD installed and running
- Helm v3 installed
- Application and Helm chart pushed to a GitHub repo
- Docker image pushed to Docker Hub or container registry
Step1:- Setup Argo CD and Connect GitHub Repository
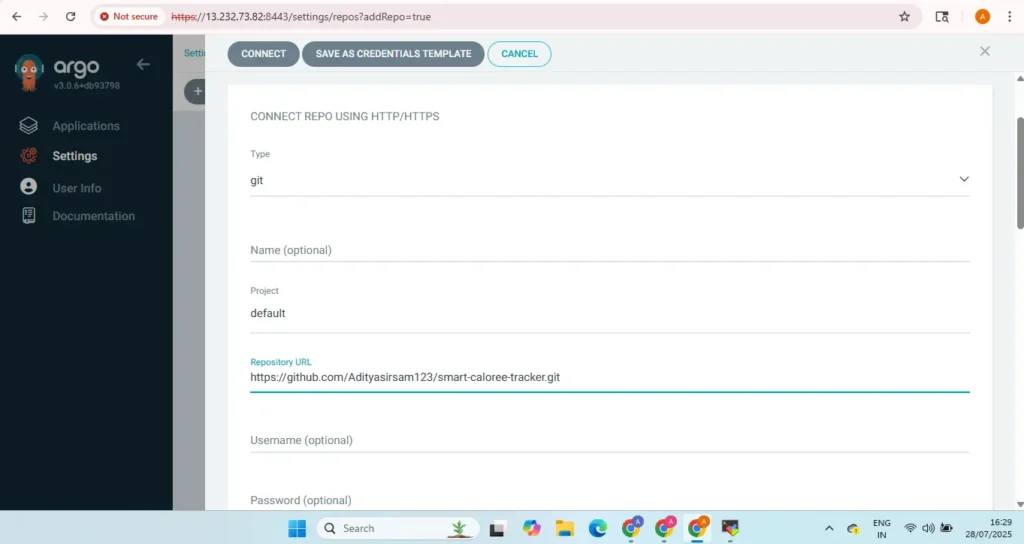
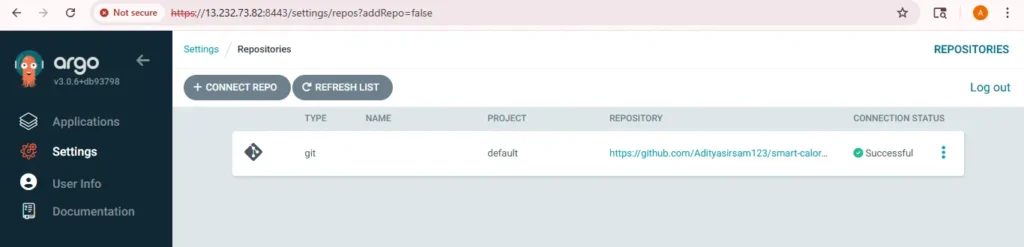
1. Add GitHub Repo to Argo CD
Go to argocd settings→ Repositories→Add repo
provide your repo url and version control login credential and click on connect repo
2.Create Application via ArgoCD Web UI
- Open the ArgoCD Web UI in your browser (e.g.,
http://<argocd-server-url>). - Log in with your username and password (default username:
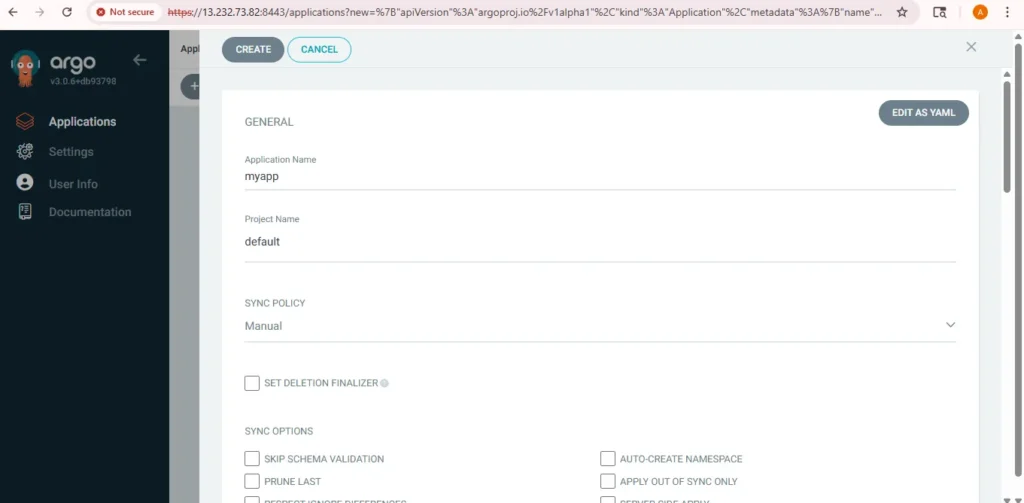
admin). - Click on “+ NEW APP” (top-left corner).
- Fill out the following details:
- Application Name: e.g.,
my-appProject: defaultSync Policy: Manual or Automatic (choose as needed)
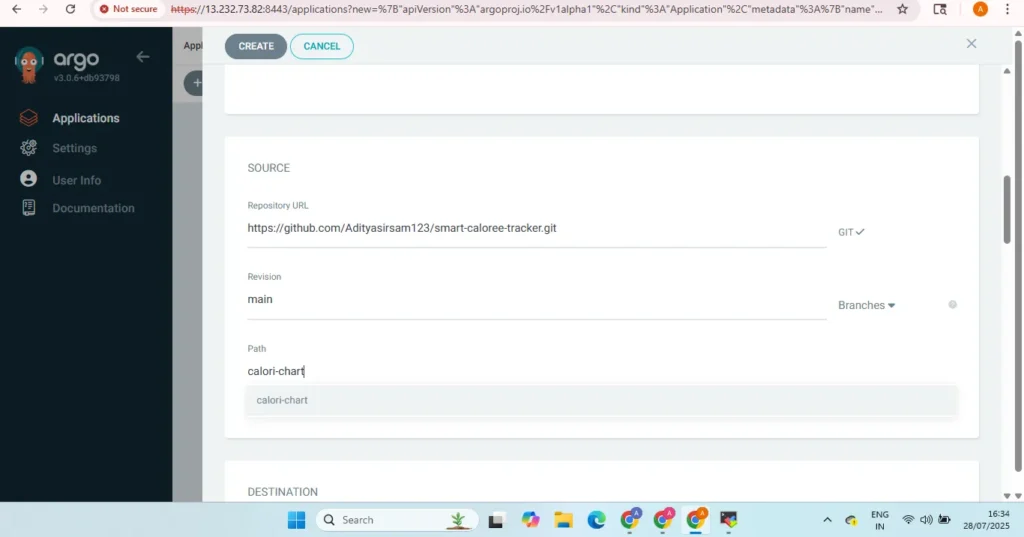
- Repository URL: Git URL containing Helm or K8s manifests
- Revision:
HEADor specific Git branch/tag (e.g.,main) - Path: Relative path in the repo to the manifests/chart
- Cluster: Usually
https://kubernetes.default.svc - Namespace: e.g.,
defaultormy-namespace
- Application Name: e.g.,
5.Click Create.
ArgoCD will now list your application, and you can sync or monitor it from the dashboard.
Let me know if you want a screenshot-based step or CLI version as well.
3.Rolling Update Strategy in Helm Template
Inside calori-chart/templates/deployment.yaml:
strategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
maxSurge: 1
maxUnavailable: 0
This ensures zero downtime deployment: old pods are replaced one at a time.
4.Deploy the App via Argo CD
After pushing changes to GitHub:
- Open Argo CD UI (
kubectl port-forward svc/argocd-server -n argocd 8080:443) - Login with
adminuser - Find your
calori-chartapp - Click Sync or wait for Auto Sync if enabled
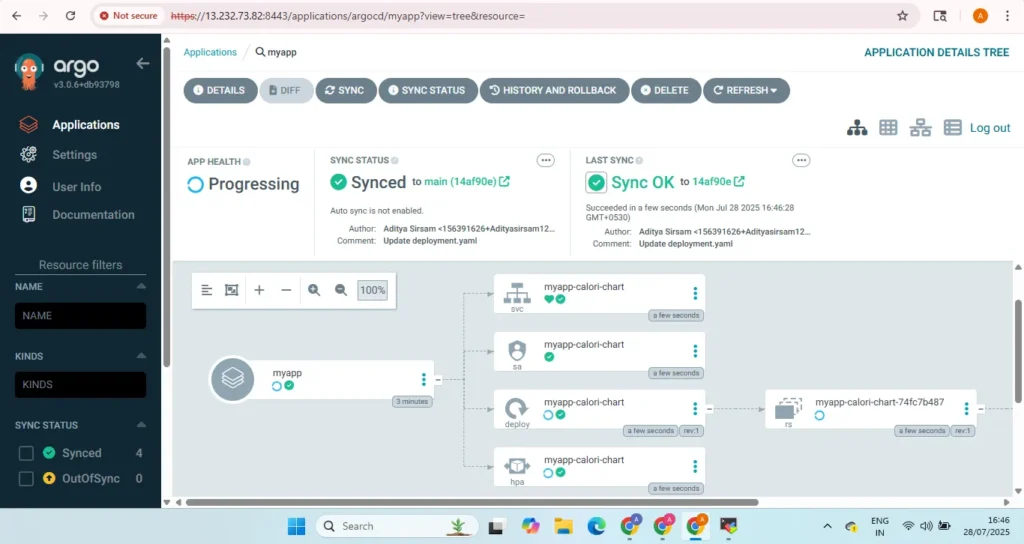
5.Verify Rolling Update Strategy via Argo CD
Trrough argocd the deployed resourses are
A. Trigger a Rolling Update via Git Push
Make a small change in your Helm chart Git repo (e.g., image tag change) and push it.
Example: Modify values.yaml in your Helm chart
image:
repository: aadityasirsam/caloritracker1
tag: v1 # <-- Change this latest to v1Then commit and push:
git add .
git commit -m "Update image tag to trigger rolling update"
git push origin main.B. Watch Argo CD Apply the Change
Go to Argo CD UI (use kubectl port-forward if needed): kubectl port-forward svc/argocd-server -n argocd 8443:443
C. Observe the Rolling Update Behavior
1.Live Pod Transition (From Argo CD UI)
- In the application tree, click the Deployment
- Check the new ReplicaSet being created
- You’ll see old pods terminating and new ones spinning up one-by-one
rollback and history
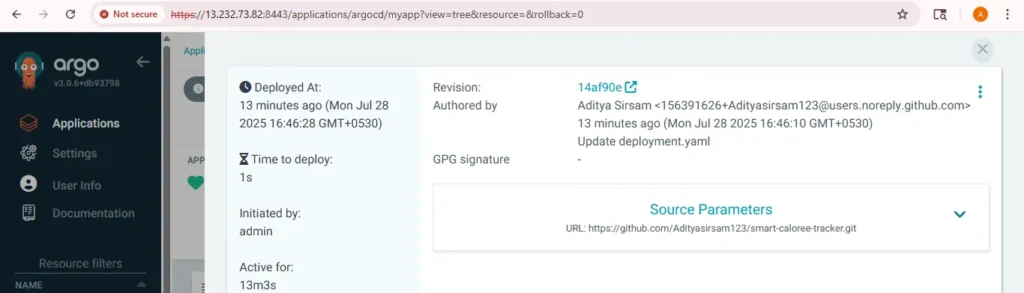
now update your values .yaml and change the version
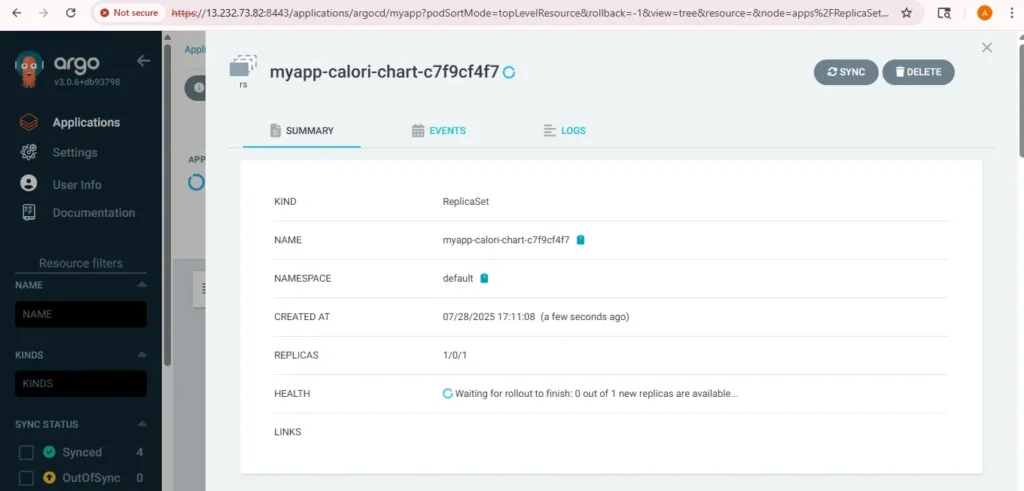
And resynck the argocd app
2. Rolling Update Successfully Applied via Argo CD
Let’s break down your observations:
Deployment & Rollout Status
kubectl rollout status deployment.apps/myapp-calori-chartOutput:
deployment "myapp-calori-chart" successfully rolled outThis confirms the rolling update was completed without error or downtime.
Rollout History
kubectl rollout history deployment.apps/myapp-calori-chartOutput:
REVISION CHANGE-CAUSE
1 <none>
2 <none>There are two revisions, meaning the deployment has been updated once — consistent with a rolling update (e.g., due to a new image or config pushed via Argo CD).
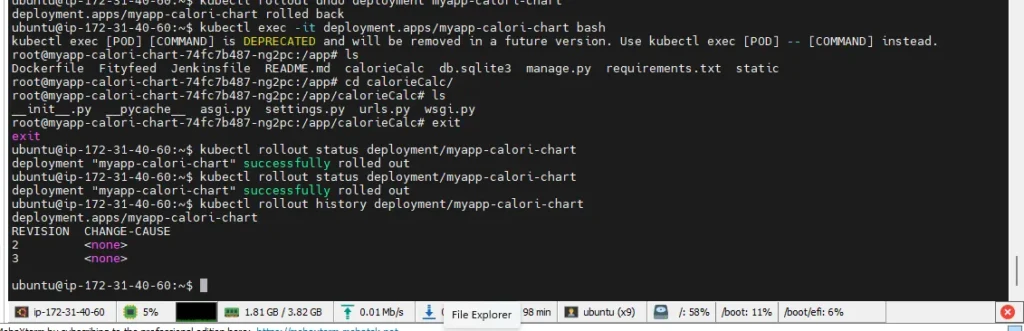
3.Roll Back to Previous Version (Revision 1)
Step 1: Run the Undo Command
kubectl rollout undo deployment/myapp-calori-chartThis will revert the deployment back to revision 1 (your original version).
Note: By default, this rolls back to the previous revision.
Step 2: Watch the Rollback in Progress
kubectl rollout status deployment/myapp-calori-chartExpected output:
deployment "myapp-calori-chart" successfully rolled outStep 3: Confirm Rollout History
kubectl rollout history deployment/myapp-calori-chartYou’ll now see:
REVISION CHANGE-CAUSE
1 <none>
2 <none>
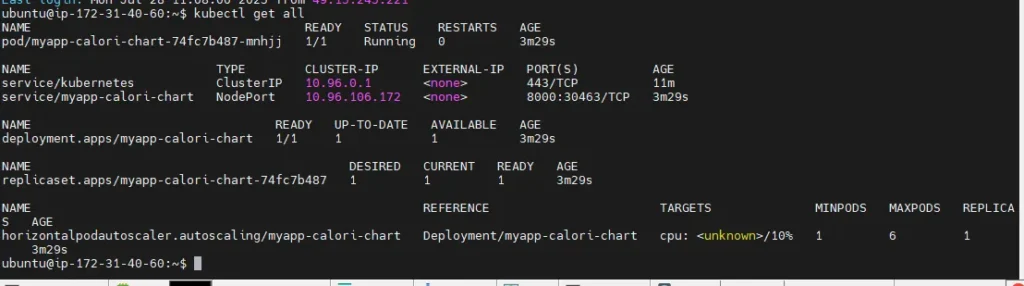
3 <none> <-- rollback actionYou can inspect the current state with
kubectl get rs
kubectl get pods -l app.kubernetes.io/name=myapp-calori-chart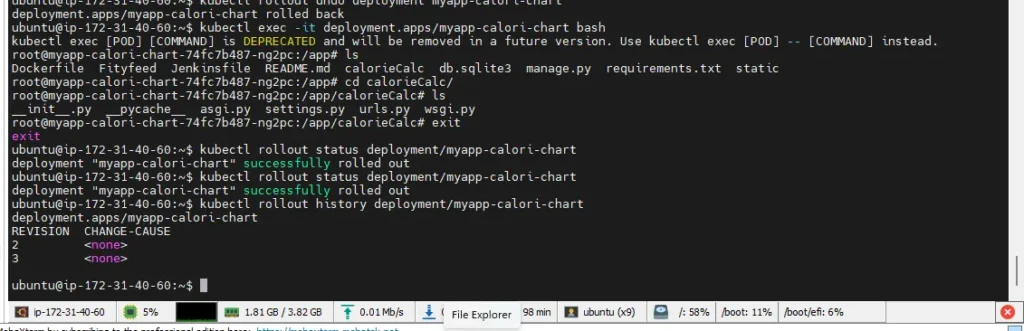
Conclusion
Using Argo CD with Helm, combined with a rolling update strategy and HPA, simplifies Kubernetes deployments while enhancing reliability and scalability. With GitOps-driven workflows, any change in your Git repository automatically syncs to your cluster, reducing manual intervention and human error. You now know how to:
- Configure and deploy Helm charts via Argo CD
- Monitor and perform rolling updates without downtime
- Implement automatic scaling with HPA
- Roll back to previous versions when necessary
This approach ensures a fully automated, scalable, and maintainable deployment pipeline that aligns with modern DevOps and GitOps best practices


