In modern DevOps practices, speed and efficiency are everything. Developers push code frequently, and Jenkins pipelines must handle multiple builds without slowing down. This is where Parallel Builds come into play.
Parallel builds allow Jenkins to run multiple stages or jobs at the same time, rather than sequentially. This drastically reduces build time and improves delivery speed — especially in large-scale projects.
In this blog, we’ll cover everything about Parallel Builds in Jenkins, including setup, pipeline examples, and best practices.
What Are Parallel Builds in Jenkins?
In a typical Jenkins pipeline, stages are executed sequentially — meaning one after another. For example:Build → Test → Deploy
This approach works fine for small projects, but as applications grow larger and teams become more distributed, sequential execution starts to slow everything down. If one stage takes too long, all the others must wait. This becomes a bottleneck in Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) pipelines where speed and feedback are critical.
Now, imagine your application has several independent components — such as a frontend, backend, and a database service. Each one can be built and tested separately. Running them one by one wastes valuable time and computing resources.
That’s where Parallel Builds in Jenkins come in.
Parallel builds allow Jenkins to execute multiple stages at the same time, instead of waiting for one to finish before starting the next. This parallelism is especially powerful when working with microservices, multi-language projects, or cross-platform testing.
real-world examples of how parallel builds can help:
- Run Unit and Integration Tests Together: You can execute different types of tests in separate branches at the same time — saving you from waiting for one test suite to finish before starting the other.
- Build Frontend and Backend Simultaneously: For full-stack or microservice applications, you can build multiple services in parallel pipelines. While the backend compiles, the frontend can bundle its code at the same time.
- Test Across Different Environments: Jenkins can spin up parallel builds across different operating systems (Linux, Windows, macOS) or different runtime versions (like Node.js 16 and Node.js 18) to ensure your application behaves consistently everywhere.
This kind of automation drastically reduces total build time, improves feedback cycles, and enables faster delivery of updates. For example, a pipeline that takes 30 minutes sequentially could often complete in 10 minutes or less with parallel execution — freeing up Jenkins resources and giving developers results faster.
In essence, Parallel Builds = Faster Feedback + Better Resource Utilization + Improved Developer Productivity.
Prerequisites
Before implementing parallel builds, make sure you have:
Jenkins installed and running
A working Jenkinsfile or Declarative Pipeline setup
Proper agents (nodes/slaves) configured if you plan to distribute builds
Required plugins:
Pipeline Plugin
Step-by-Step Implementation of Parallel Builds
Let’s create a Jenkins declarative pipeline that runs three tasks in parallel:
- Build the code
- Run Unit Tests
- Run Integration Tests
Step 1: Create a Jenkins Pipeline Job
- Open Jenkins Dashboard
- Click on “New Item” → “Pipeline”
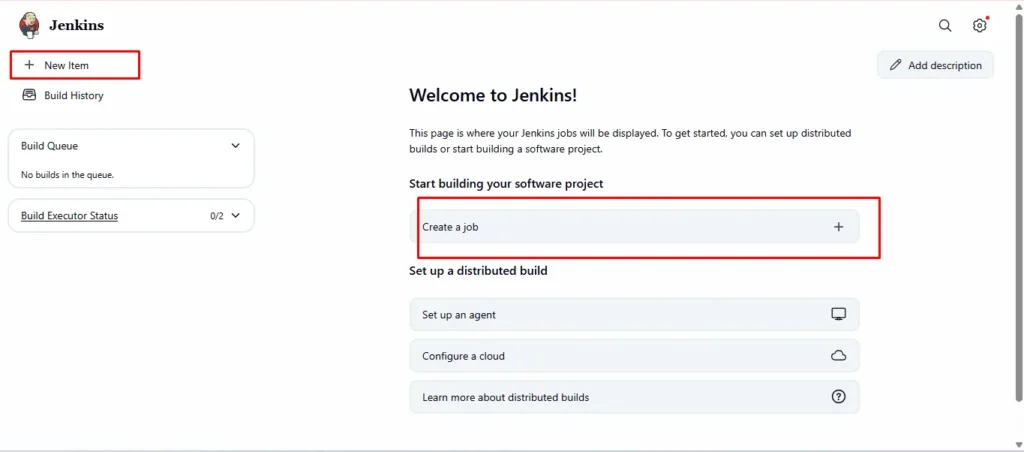
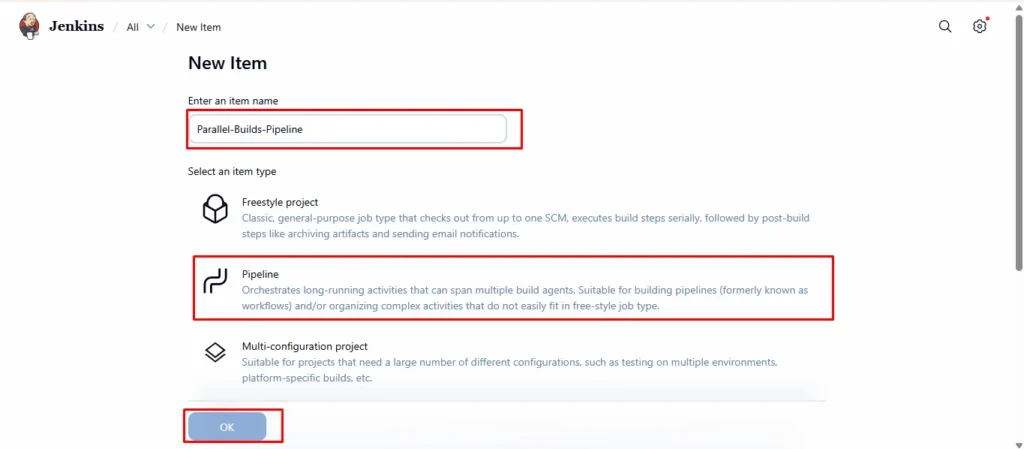
3.Name it something like Parallel-Builds-Pipeline
4.Choose Pipeline → Click OK
Step 2: Define Jenkinsfile (Pipeline Script)
Here’s a sample Jenkinsfile that demonstrates parallel execution:
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Build') {
steps {
echo 'Building the application...'
sh 'sleep 5' // simulate build time
}
}
stage('Test in Parallel') {
parallel {
stage('Unit Tests') {
steps {
echo 'Running Unit Tests...'
sh 'sleep 3'
echo 'Unit Tests Completed '
}
}
stage('Integration Tests') {
steps {
echo 'Running Integration Tests...'
sh 'sleep 5'
echo 'Integration Tests Completed '
}
}
stage('UI Tests') {
steps {
echo 'Running UI Tests...'
sh 'sleep 7'
echo 'UI Tests Completed '
}
}
}
}
stage('Deploy') {
steps {
echo 'Deploying the application...'
sh 'sleep 4'
echo 'Deployment Completed '
}
}
}
post {
always {
echo 'Cleaning up after pipeline...'
}
}
}
- Scroll down to the Pipeline section and select “Pipeline script”
- Paste the below Jenkinsfile code
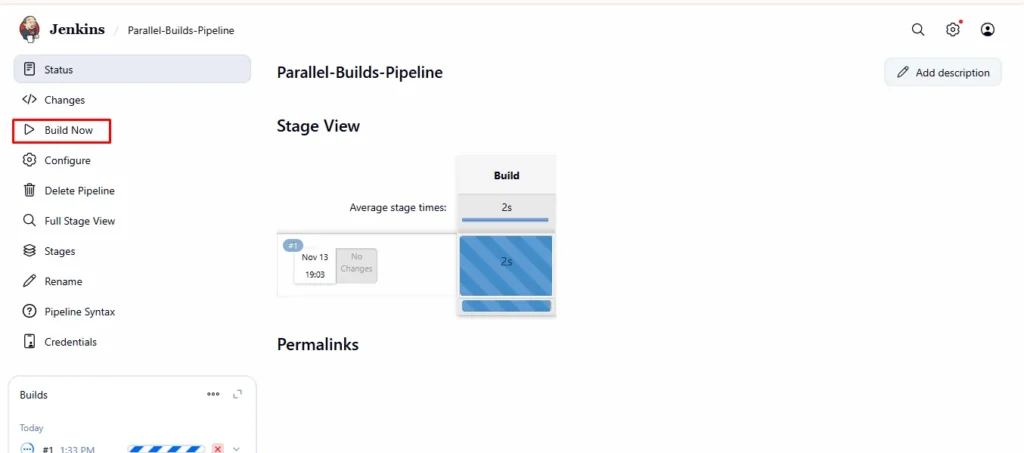
Step 3: Configure Jenkins Job
- In Jenkins Dashboard → open the pipeline you created
- Click on Build Now
Best Practices for Parallel Builds in Jenkins
Parallel builds are powerful, but they must be designed carefully for efficiency and reliability. Follow these tips to make your pipelines cleaner and more scalable:
- Keep stages independent
Each parallel stage should run independently without depending on files, data, or outputs from another stage. Shared resources can cause conflicts or failures when stages run simultaneously.
Example: Don’t make two parallel stages write to the same log file or modify the same directory. - Use labels to distribute workloads across agents
If you have multiple Jenkins agents (nodes), you can assign specific stages to specific machines.
This allows Jenkins to distribute workloads — for example, running tests on Linux, Windows, and macOS agents in parallel.stage('Linux Build') { agent { label 'linux' } steps { echo "Building on Linux node" } } - Combine with Matrix Builds for platform or OS-based testing
Matrix builds allow you to run the same stage with different parameters (like OS, Python version, or browser). When combined with parallelism, you can achieve massive test coverage quickly.
Example: Test your app on multiple operating systems or database versions at once. - Monitor performance using the Blue Ocean plugin
Jenkins Blue Ocean provides a visual interface for pipelines. It displays parallel stages side by side, helping you easily identify which stage takes more time or fails often.
This visualization is extremely useful for debugging and optimization. - Use timeouts to prevent long-running jobs from hanging
Sometimes, a single stage may get stuck due to network or environment issues. Always use thetimeoutdirective to automatically stop long-running stages.stage('Test') { steps { timeout(time: 5, unit: 'MINUTES') { sh './run_tests.sh' } } }This keeps your Jenkins queue free and prevents unnecessary resource usage.
Conclusion
Parallel Builds in Jenkins are one of the most effective ways to accelerate your CI/CD pipelines. By allowing multiple stages or jobs to run simultaneously, teams can significantly reduce build times, improve feedback loops, and utilize Jenkins resources more efficiently.
Whether you’re building microservices, running multiple test suites, or deploying across environments, parallelism ensures your delivery process remains fast, scalable, and reliable. With just a few lines in your Jenkinsfile, you can transform a traditional linear pipeline into a high-performance, concurrent workflow that better fits modern DevOps practices.
In short, Parallel Builds = Faster Feedback + Better Resource Utilization + Continuous Delivery Efficiency.
Start simple — even with basic echo commands — and then gradually scale your pipelines by integrating real build, test, and deploy tasks. Once implemented, you’ll quickly see how parallel execution can make a big difference in your software delivery speed and team productivity.


