Continuous Integration, often called CI, is an important part of the software development process, especially in DevOps practices. It allows developers and teams to work together more efficiently by regularly adding (integrating) their code changes into a shared repository — usually managed by a version control system like Git or GitHub.
In simple terms, Continuous Integration helps make sure that everyone’s code works well together. Whenever a developer makes changes or adds a new feature, CI automatically checks if the code still runs properly by building and testing it. This helps in catching bugs early, before they become big problems.
With CI, teams can automate project workflows such as building, testing, and deploying software across different environments like Development (Dev), Testing (QA), Staging, and Production (Prod). This automation saves time, reduces manual effort, and ensures consistency across all stages.
Overall, Continuous Integration makes it easier for teams to collaborate, track changes, detect issues quickly, and deliver high-quality software faster. It builds trust in the codebase and helps maintain a smooth, error-free development process.
What Continuous Integration (CI) Does?
Continuous Integration (CI) is a process that helps developers automate and manage their software development workflow. It follows a few simple but important steps — planning, coding, making changes or merging code, checking results, and pushing updates.
In traditional development, developers would write a lot of code and only test it at the end, which often caused big errors and delays. CI solves this problem by allowing developers to frequently merge small pieces of code into a shared repository (like GitHub). Each time code is merged, the CI system automatically builds and tests it to ensure everything still works correctly.
To set up CI for your project, you first need to choose the right tools and services that fit your team’s needs. These tools help you automate different stages of development — from writing and storing code to testing and deployment.
Here are some of the most popular CI tools used by organizations today:
Jenkins: One of the most widely used open-source CI tools, known for its flexibility and plugins.
CircleCI: A fast, cloud-based CI tool that integrates easily with GitHub and Bitbucket.
GitHub Actions: Built directly into GitHub, it lets you automate workflows like building, testing, and deploying code.
Azure Pipelines: Part of Microsoft Azure DevOps, great for building and deploying across multiple platforms.
GitLab CI/CD: An integrated tool within GitLab that automates the whole development lifecycle.
Bitbucket Pipelines: A simple, cloud-based CI/CD tool for teams using Bitbucket repositories.
Using these CI tools, teams can easily manage their source code, track versions, run automated builds and tests, and release software faster and with fewer errors. In short, Continuous Integration helps make the software development process smoother, faster, and more reliable for everyone involved.
Here is the quick Overview of Continuous Integration Workflow:
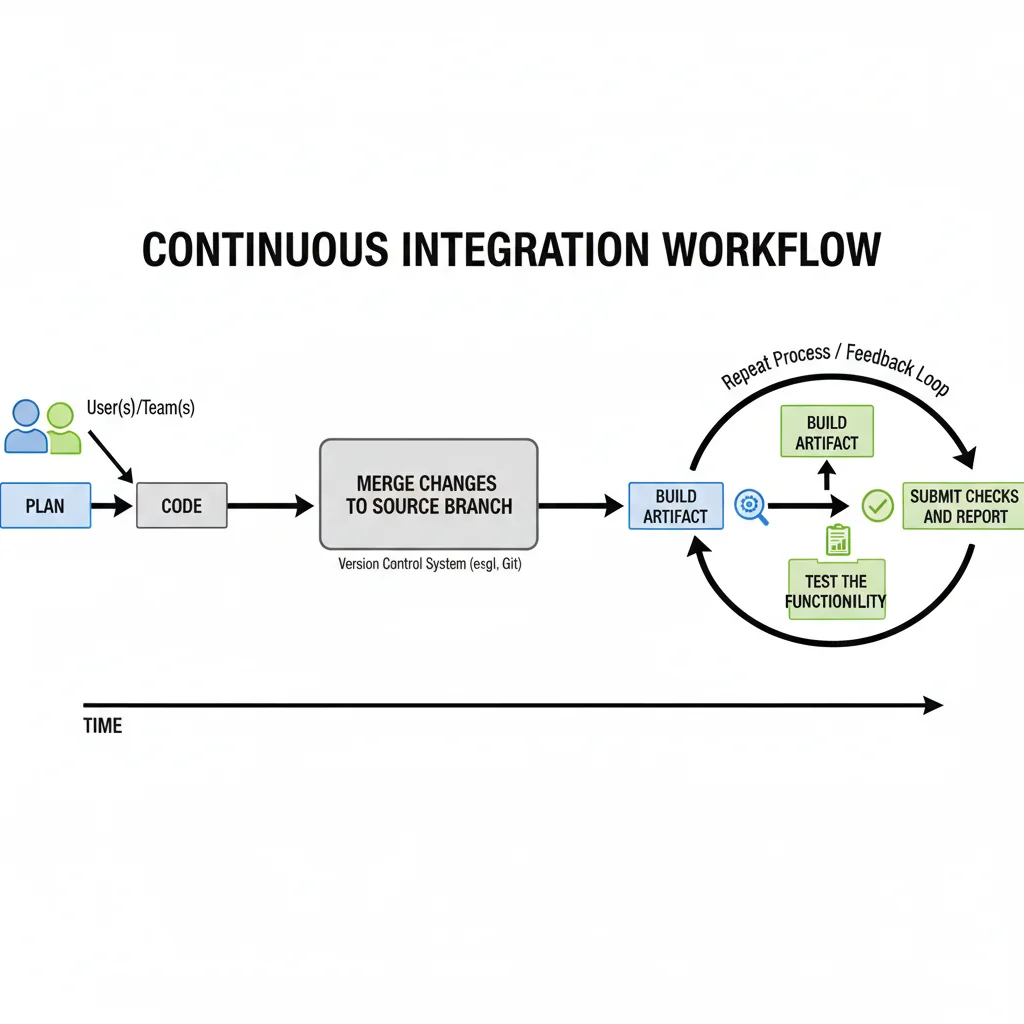
Why is Continuous Integration Needed?
Continuous Integration (CI) is needed because it helps software teams work faster, smarter, and with fewer mistakes. In traditional development, developers would write large amounts of code and test it only at the end — which often caused bugs, conflicts, and delays. CI solves this by allowing developers to frequently merge small code changes, which are automatically built, tested, and verified.
By adopting CI, teams can improve code quality step by step. Since the process is automated, developers don’t need to spend too much time setting up environments or manually testing code. Instead, they can focus more on writing new features and fixing bugs — the tasks that really matter for improving the product.
Another major reason CI is needed is that it helps catch bugs early — before they become big issues. Each time new code is added, the CI system automatically checks if the application still works properly. This makes it easier to detect and fix problems quickly, rather than discovering them later in production when they are harder and more expensive to fix.
Continuous Integration also brings transparency and visibility to the entire development process. Every team member can see what’s happening — whether a build passed, failed, or needs attention. This visibility helps teams track progress, identify bottlenecks, and find areas that need improvement.
How Does Continuous Integration Work?
Imagine you have a code repository (like GitHub or GitLab) with a main branch — let’s call it the release branch. This is where all the latest and stable code is stored.
Now, whenever you or your teammates make any changes to the project — like adding a new feature, fixing a bug, or updating existing code — you commit those changes to the repository.
Once the code is pushed, the CI tool automatically detects the new changes. It then performs a few important steps:
- Fetches the latest code from the repository.
- Builds the project — meaning it compiles and prepares the code into a usable format (called an artifact).
- Runs automated tests to check if everything is working properly.
- If the build and tests are successful, the CI tool can automatically deploy the application to an environment — like Development, Testing, or Staging — for further review.
If any step fails, the CI tool immediately notifies the team (through email, Slack, or the CI dashboard), so the issue can be fixed quickly.
Continuous Integration (CI) Benefits
Continuous Integration (CI) makes the software development process easier, faster, and more reliable by automating repetitive tasks. Instead of manually building, testing, and deploying code, CI automates these steps every time a developer pushes new code. This saves time, reduces human errors, and improves overall code quality.
- Reduce Manual Tasks:
CI eliminates the need to manually build or test code every time a developer makes a change. It automatically compiles the code, runs tests, and checks for errors, which saves a lot of time and effort. Developers can focus on writing new features instead of performing repetitive setup work. - Code Integrations and Improvements:
CI tests each code change automatically as soon as developers push it. When the system finds a bug, it instantly alerts the team. This early feedback allows developers to fix problems quickly and keep the codebase stable. Over time, it enhances code quality and reliability. - Better Team Collaboration:
CI helps teams work together smoothly. It allows everyone to share code and integrate their updates without conflicts. This boosts communication, prevents code issues, and ensures that the project runs consistently across all contributions. - Visibility and Transparency:
CI tools show the full picture of the development process. Developers can see which builds pass or fail and track every code change. This visibility helps teams spot issues faster, track progress, and improve decision-making. - Faster Release:
When you combine CI with Continuous Deployment (CD), your application goes live automatically whenever you push new code to the main branch. This leads to faster delivery, quick updates for users, and a more efficient release cycle.
Continuous Integration vs Continuous Deployment vs Continuous Delivery
Continuous Integration(CI), Continuous Deployment (CD) or Continuous Delivery(CD) are all part of the software development process.
| Continuous Integration(CI) | Continuous Delivery (CD) | Continuous Deployment (CD) |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Integration(CI) is a process to integrate code changes in a repository frequently and automatically built, tested, and merged into the main branch. | Continuous Delivery (CD) is a process to build on Continuous Integration(CI) by automating the deployment process delivering the content or features live to different environments. | Continuous Deployment (CD) is a process to deploy the software based on tests performed from Continuous Delivery (CD) and moving the changes to live environment or production environment. |
| Automation for: Building and Testing | Automation for: deployment of code changes. | Automation for: deployment of code changes to production based on tests passed. |
| Release Type: Manual(User Chnages) | Release Type: It can Manual or Automated | Release Type: Fully Automated. |
Conclusion
Continuous Integration (CI) is one of the most powerful and essential practices in modern software development, especially in DevOps environments. It helps teams work smarter by automating repetitive tasks, catching bugs early, and ensuring that code changes integrate smoothly into the main application. With CI, developers can focus more on innovation and problem-solving instead of spending time on manual builds, testing, or deployments.
By combining CI with Continuous Delivery (CD) and Continuous Deployment, organizations can achieve a complete automation workflow — from writing code to releasing it into production. This not only improves code quality and team collaboration but also allows for faster and more reliable software releases.
In short, Continuous Integration is not just a tool or process — it’s a culture of continuous improvement that ensures your software remains stable, up-to-date, and ready for deployment at any time. It plays a key role in building modern, efficient, and high-performing DevOps pipelines


