In today’s fast-paced software development world, efficient and reliable deployment methods are essential. GitOps, which uses Git as a foundational element for managing infrastructure and applications, offers a transformative approach. ArgoCD, a leading Kubernetes-native tool, exemplifies GitOps by automating and scaling deployments. This post will explore GitOps, the significance of ArgoCD for DevOps, and its components and architecture for effective Kubernetes application management.
What is ArgoCD?
ArgoCD is a declarative, GitOps continuous delivery tool that is specifically designed for the orchestration and management of Kubernetes applications. It stands as a cornerstone in the GitOps landscape, offering a seamless bridge between the declarative configuration of applications and their deployment in Kubernetes clusters. Here are some of the core features and capabilities of ArgoCD:
Automatic Sync: It automatically syncs applications with their desired state in the Git repository, ensuring consistency and reliability.
Declarative Setup: ArgoCD uses Git repositories as the source of truth for defining the desired application state in Kubernetes.
Self-Healing Deployments: ArgoCD continuously monitors deployed applications and heals them by automatically applying the desired state from Git, thus reducing downtime and manual intervention.
Visual UI and CLI: Offers a user-friendly UI and a powerful CLI, catering to different preferences for managing deployments.
ArgoCD Components and Architecture
ArgoCD follows a clean, modular architecture built around a core set of components. Each component plays a specific and crucial role, so together they enable smooth, declarative continuous delivery using the GitOps methodology.
To truly leverage ArgoCD in your Kubernetes clusters, you first need to understand these components and how they interact with one another.
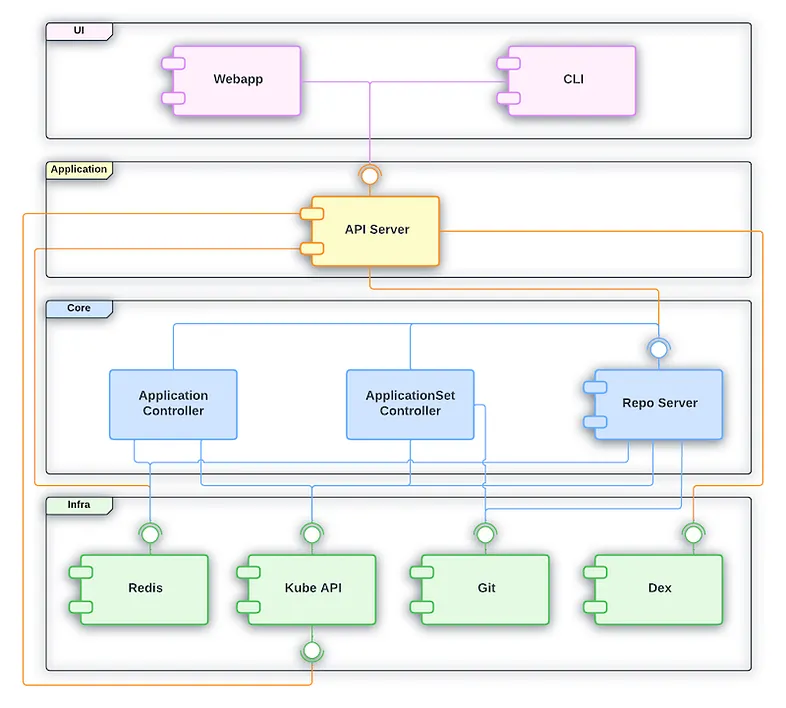
There are 4 logical layers represented in the diagram:
UI: This is the part you see and interact with — like the ArgoCD dashboard or the CLI.
It allows users to check application status, sync apps, view logs, and manage deployments.
Application: This layer provides the features and functions needed by the UI.
It helps the UI display application details, projects, sync options, and health status..
Core: This layer contains the main logic of ArgoCD.
This is where the GitOps magic happens — comparing Git with the cluster, detecting drift, and syncing..
Infra: This is the foundation on which ArgoCD works. It includes Kubernetes, Git repositories, cluster tools, and networking.
Core Components:
API Server
The API server is a gRPC/REST server which exposes the API consumed by the Web UI, CLI, and CI/CD systems. It has the following responsibilities:
- application management and status reporting
- invoking of application operations (e.g. sync, rollback, user-defined actions)
- repository and cluster credential management (stored as K8s secrets)
- authentication and auth delegation to external identity providers
- RBAC enforcement
- listener/forwarder for Git webhook events
Repository Server
The repository server is an internal service which maintains a local cache of the Git repository holding the application manifests. It is responsible for generating and returning the Kubernetes manifests when provided the following inputs:
- repository URL
- revision (commit, tag, branch)
- application path
- template specific settings: parameters, helm values.yaml
Application Controller
The application controller is a Kubernetes controller which continuously monitors running applications and compares the current, live state against the desired target state (as specified in the repo). It detects OutOfSync application state and optionally takes corrective action. It is responsible for invoking any user-defined hooks for lifecycle events (PreSync, Sync, PostSync)
Dex Server: An optional component that provides an identity federation service. Dex integrates with external identity providers (such as LDAP, SAML, GitHub, and others) to offer unified authentication and access control for ArgoCD.
Architecture of Argocd:
ArgoCD delivers a highly scalable and resilient architecture that keeps applications in their desired state at all times. Here’s how it works:
- Git as the Source of Truth First, developers declare the entire desired state — manifests, configurations, and environment settings — directly in a Git repository. Consequently, Git becomes the single, version-controlled source of truth for everyone.
- Continuous Monitoring Next, the ArgoCD Application Controller constantly compares two things: the live state of resources inside the Kubernetes cluster and the desired state defined in Git. As soon as it detects any difference, it springs into action.
- Automatic Synchronization Whenever a discrepancy appears — whether from a new commit, a manual change, or drift — ArgoCD immediately reconciles the cluster. For example, it applies new manifests, scales replicas, or even rolls back unwanted changes, all without human intervention.
- Self-Healing Capabilities Moreover, ArgoCD actively heals the cluster. If someone accidentally deletes a resource or an external process modifies it, ArgoCD quickly detects the drift and restores the correct state. As a result, applications stay reliable and consistent across development, staging, and production environments.
- Visibility and Control Finally, teams gain full transparency through the ArgoCD web UI and CLI. They can instantly see which applications are healthy, in sync, or out of sync. Additionally, detailed diff views and historical logs make troubleshooting fast and precise.
Conclusion
ArgoCD represents a paradigm shift in how we approach Kubernetes application management. By tightly coupling deployment processes with the GitOps methodology, it transforms the complex task of cluster orchestration into a streamlined, automated, and auditable workflow.
The power of ArgoCD lies not just in its ability to automate deployments, but in its robust architecture that ensures consistency, visibility, and resilience. With features like self-healing capabilities and a single source of truth in Git, DevOps teams can move away from manual, error-prone “kubectl” commands and embrace a future where infrastructure is as version-controlled and reliable as application code.
As organizations continue to scale their containerized environments, adopting a tool like ArgoCD is no longer just an option—it is a strategic necessity for maintaining operational excellence and delivering software with confidence.


