Introduction
Running tests manually often leads to delayed bug detection and inconsistent reporting. Therefore, automating test execution becomes essential for maintaining application stability. In this guide, you will learn how to schedule a nightly pipeline in GitLab using an EC2 runner, execute tests automatically, and generate downloadable reports.
By the end of this tutorial, your pipeline will run daily without manual intervention.
Why You Should Schedule a Nightly Pipeline in GitLab
Manual testing creates gaps in quality assurance. As a result, issues may remain unnoticed for days. A scheduled nightly pipeline in GitLab ensures:
- Daily automated verification
- Early bug detection
- Consistent test reporting
- Zero manual triggering
Moreover, scheduled pipelines improve team productivity because developers receive fresh test results every morning.
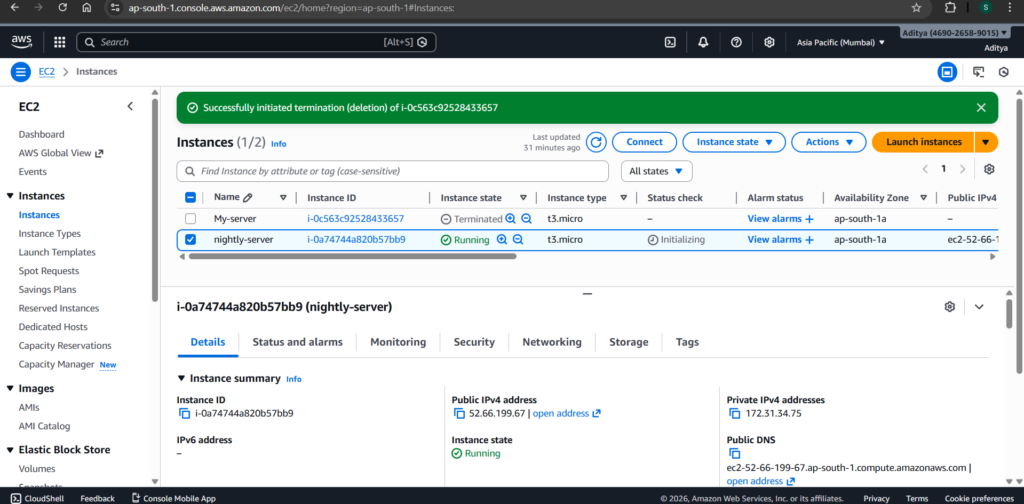
Launch an EC2 Instance
First, log in to AWS and launch a new EC2 instance.
Configuration:
- AMI: Ubuntu 24.04 LTS
- Instance Type: t3.micro
- Security Group: Allow SSH (Port 22)
- Storage: Default 8GB
After launching, connect using SSH:
ssh -i your-key.pem ubuntu@your-public-ipInstall Required Dependencies
Next, update your system and install necessary tools.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
sudo apt install git -y
sudo apt install docker.io -yThen enable Docker:
sudo systemctl start docker
sudo systemctl enable docker
sudo usermod -aG docker ubuntuReconnect to apply Docker group changes.
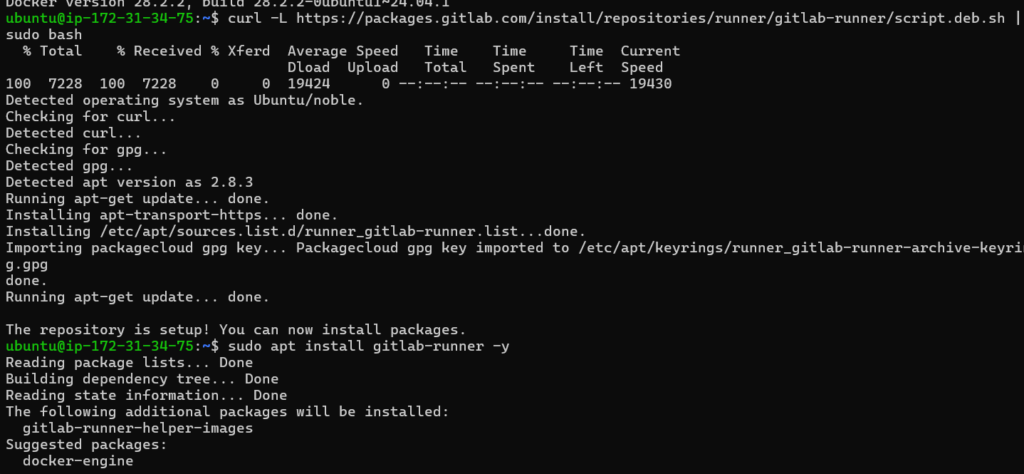
Install GitLab Runner on EC2
Now install GitLab Runner.
curl -L https://packages.gitlab.com/install/repositories/runner/gitlab-runner/script.deb.sh | sudo bash
sudo apt install gitlab-runner -yVerify installation:
gitlab-runner --version
Register the EC2 Runner
Open your GitLab project and navigate to:
Settings → CI/CD → Runners
Copy the registration token.
Then run:
sudo gitlab-runner registerProvide the following:
- GitLab URL
- Registration token
- Description: ec2-runner
- Executor: docker
- Default image: python:latest
At this stage, your EC2 instance can execute pipelines.
Create a Sample Application and Test
Create the following files in your repository:
app.py
def add(a, b):
return a + btest_app.py
from app import add
def test_add():
assert add(2, 3) == 5requirements.txt
pytestCommit and push these files to GitLab.
Repository Structure
Before running the scheduled nightly pipeline in GitLab, your project should follow a clean structure. A well-organized repository improves readability and simplifies pipeline execution.
Here is the final directory layout:
nightly-test-pipeline/
│
├── app.py
├── test_app.py
├── requirements.txt
└── .gitlab-ci.ymlConfigure the GitLab CI Pipeline
Create a .gitlab-ci.yml file in the root directory.
stages:
- test
- report
variables:
REPORT_FILE: "test_report.txt"
test_job:
stage: test
image: python:latest
script:
- pip install -r requirements.txt
- pytest --maxfail=1 --disable-warnings > $REPORT_FILE
artifacts:
paths:
- $REPORT_FILE
expire_in: 1 week
report_job:
stage: report
script:
- echo "Test Report Generated Successfully"
dependencies:
- test_jobThis configuration defines two clear stages. Additionally, it stores the generated report as a pipeline artifact.
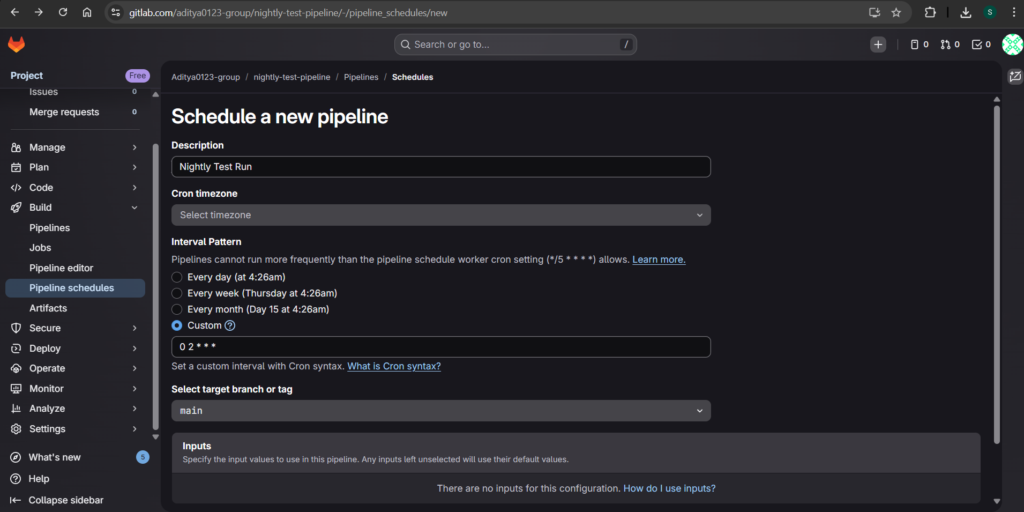
Schedule the Nightly Pipeline in GitLab
Navigate to:
CI/CD → Pipeline Schedules
Click New Schedule and configure:
- Description: Nightly Test Run
- Branch: main
- Cron:
0 2 * * *This cron expression runs the pipeline daily at 2 AM.
Once saved, GitLab automatically triggers the pipeline at the scheduled time.
Verify the Scheduled Pipeline
After the scheduled time, open:
CI/CD → Pipelines
The pipeline source should display:
ScheduleThen confirm:
- Test stage executed
- Report generated
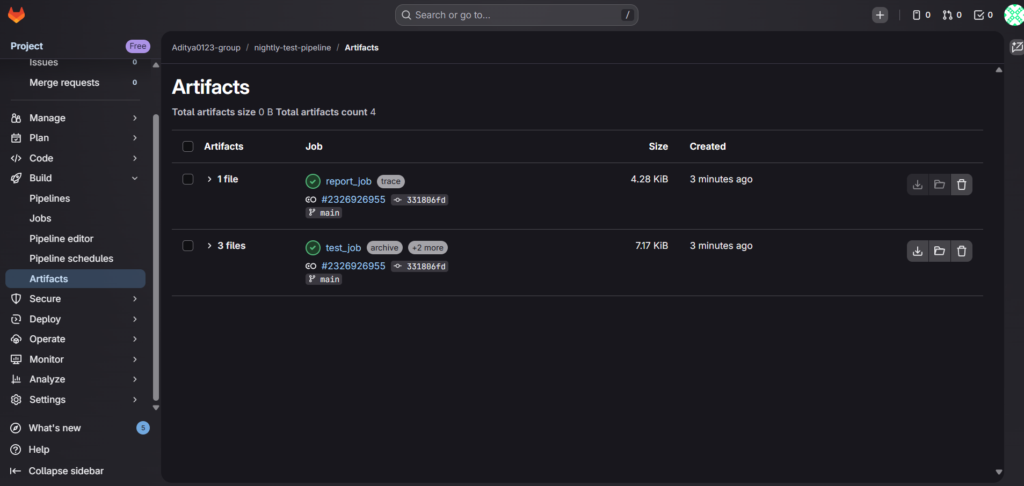
- Artifact available for download
If all conditions are satisfied, your scheduled nightly pipeline in GitLab works correctly.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Many beginners encounter similar issues. However, you can avoid them easily.
- Do not rely only on push-triggered pipelines
- Avoid force pushing to protected branches
- Always verify the pipeline source shows “Schedule”
- Ensure artifacts are stored properly
Careful configuration ensures a smooth CI/CD workflow.
Final Thoughts
Automating test execution through a scheduled nightly pipeline in GitLab significantly improves reliability. Instead of depending on manual testing, your system now validates the application every day without intervention.
Most importantly, the team gains consistent reports and faster feedback cycles.
Start implementing scheduled pipelines today and strengthen your DevOps practices.
Conclusion
Automating test execution through a scheduled nightly pipeline in GitLab transforms the way teams maintain software quality. Instead of relying on manual test runs, you now have a system that verifies your application every day without intervention.
More importantly, scheduled pipelines provide consistent reporting, faster feedback cycles, and improved reliability. By integrating an EC2 runner, you gain complete control over your CI/CD environment while keeping costs minimal.
Implementing this setup strengthens your DevOps foundation and prepares you for real-world production workflows. Start scheduling your nightly pipelines today and let automation handle the verification process for you.