Cloud security is as much about keeping secrets as it is about protecting data. In Amazon Web Services (AWS), however, the term secretshas a special meaning, which deals with credentials for access and use of data. Encryption keys keep secrets too, but in a different way. They scramble data to keep people from reading it. In this article, we take a look at AWS KMS vs Secrets Manager and how to manage keys and secrets in AWS.
In cybersecurity, the “CIA triad” stands for confidentiality, integrity, and availability. The services we discuss in this article were developed to maintain confidentiality by keeping private information private. But of course, they differ in their methods.
AWS Key Management Service (KMS): A Quick Definition
AWS Key Management Service (KMS) is a fully managed AWS service designed to create, manage, and control cryptographic keys across applications and services in the AWS cloud. KMS acts as a master key holder that keeps all the secret codes (encryption keys) used to secure your cloud data. By centralizing key management, AWS KMS ensures that encryption keys are properly created, stored, and used across your AWS environment.
If you want to dive deeper, AWS provides an official guide on Encryption, Cryptography, and Signing with KMS.
What Data Does AWS KMS Hide?
At its core, AWS KMS handles data encryption. Encryption takes plaintext and transforms it into unreadable ciphertext, so even if unauthorized users gain access to it, they won’t be able to make sense of it. AWS KMS secures your data by storing the cryptographic keys required for decryption. Without the right key, the encrypted data remains hidden and unreadable.
This means that with AWS KMS, your most sensitive information can be effectively hidden in plain sight.
How Does AWS KMS Work?
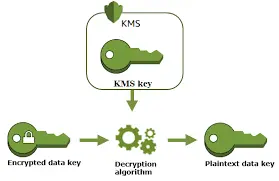
AWS KMS uses a key hierarchy model that is similar to using a lockbox with multiple keys. For example, in a vacation rental, you might use a code to unlock a box that contains the physical key for the door. In KMS, this is achieved through envelope encryption.
- A customer-managed key (CMK) encrypts your data.
- That CMK itself is encrypted using another KMS key, providing a layered security model.
AWS KMS uses the AES 256-bit GCM (Advanced Encryption Standard with Galois Counter Mode) encryption algorithm, one of the most secure methods available today. All keys are stored in Hardware Security Modules (HSMs), which are physical devices designed to safeguard cryptographic material. These HSMs are FIPS 140-2 compliant, a standard defined by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
Types of Keys in AWS KMS:
Customer managed keys | AWS managed keys | AWS owned keys | |
| Key policy | Exclusively controlled by the customer | Controlled by service; viewable by customer | Exclusively controlled and only viewable by the AWS service that encrypts your data |
| Logging | CloudTrail customer trail or event data store | CloudTrail customer trail or event data store | Not viewable by the customer |
| Lifecycle management | Customer manages rotation, deletion and Regional location | AWS KMS manages rotation (annual), deletion, and Regional location | AWS service manages rotation, deletion, and Regional location |
| Pricing | Monthly fee for existence of keys (pro-rated hourly). Also charged for key usage | No monthly fee; but the caller is charged for API usage on these keys | No charges to customer |
Client-Side vs. Server-Side Encryption:
- Client-Side Encryption (CSE): You encrypt data before sending it to AWS and manage the keys yourself.
- Server-Side Encryption (SSE): AWS handles encryption and key management automatically.
AWS KMS is highly scalable, durable, and available, ensuring secure key management across your cloud infrastructure.
How is AWS KMS Used?
AWS KMS is mainly used to protect data at rest. It enables encryption and decryption of data and also supports digital signing and verification. Both symmetric and asymmetric encryption methods are supported.
Additionally, AWS KMS integrates with AWS CloudTrail for auditing, so you can track how, when, and by whom your keys are being accessed. This provides both transparency and compliance for organizations handling sensitive information.
AWS Secrets Manager
AWS Secrets Manager is a managed service that securely stores, retrieves, and rotates secrets such as database credentials, application passwords, API keys, and OAuth tokens. Think of AWS Secrets Manager as a trusted assistant that not only stores sensitive credentials but also rotates them automatically to maintain strong security practices.
This service ensures that applications can securely access secrets without exposing them in plaintext or hardcoding them into code.
What Data Does AWS Secrets Manager Hide?
Like KMS, AWS Secrets Manager protects sensitive information, but it focuses on credentials instead of keys. The key difference is simple:
- KMS hides encryption keys
- Secrets Manager hides credentials
A helpful analogy is entering a corporate building:
- A key card gives you access to doors (like KMS keys).
- An ID badge proves your identity (like credentials in Secrets Manager).
Secrets Manager can securely store many types of credentials, including usernames, passwords, tokens, and API keys. By retrieving secrets programmatically, it prevents credentials from being exposed in plaintext, which protects against potential security breaches.
How Does AWS Secrets Manager Work?
AWS Secrets Manager enables applications to access sensitive data without embedding credentials in code. Secrets Manager integrates with AWS KMS for encryption, meaning secrets are always protected at rest.
For advanced use cases, you can configure AWS Lambda triggers to automatically rotate secrets, such as updating a database password in Amazon RDS. This eliminates the need for manual rotation and improves compliance.
Additionally, AWS CloudTrail and CloudWatch provide full auditing and monitoring of secret access, allowing you to receive alerts on suspicious activity or conduct forensic investigations after an incident.
How is AWS Secrets Manager Used?
Beyond secure storage, AWS Secrets Manager supports automatic credential rotation, which is critical for meeting compliance standards like PCI DSS or HIPAA. It also allows replication of secrets across multiple AWS regions, ensuring availability during disaster recovery scenarios.
Access to stored secrets is tightly controlled through AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM). For example, you can allow database administrators access to database credentials while restricting developers to only application secrets.
This role-based control adds another layer of fine-grained security to your AWS environment.
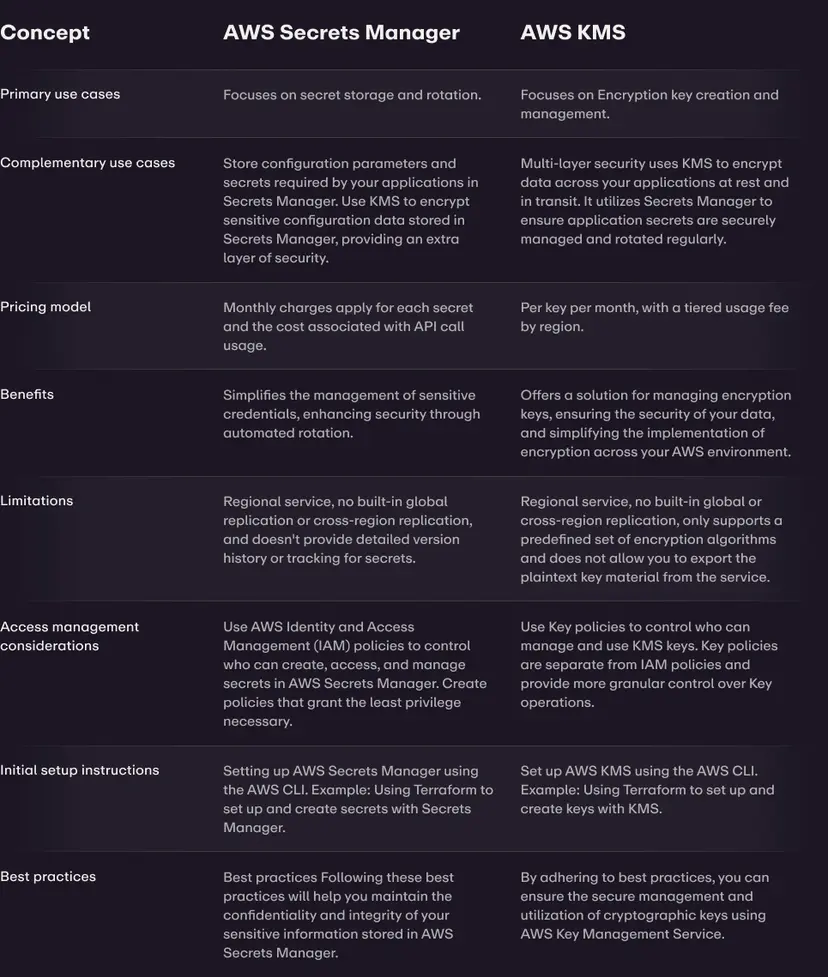
Difference Between Secret Manager And KMS
Conclusion
AWS KMS and AWS Secrets Manager serve different but complementary purposes. AWS KMS is primarily focused on encryption—creating, storing, and managing cryptographic keys used to protect sensitive data across AWS services. It does not store secrets directly but provides the backbone for secure encryption and decryption. AWS Secrets Manager, on the other hand, is designed for securely storing, managing, and automatically rotating secrets such as database credentials, API keys, and tokens. It internally uses KMS for encryption but adds secret lifecycle management and integration with applications.


