AWS(Amazon Web Services) offers a wide range of storage services that can be provisioned depending on your project requirements and use case. AWS storage services have different provisions for highly confidential data, frequently accessed data, and the not so frequently accessed data. You can choose from various storage types namely, object storage, file storage, block storage services, backups, and data migration options. All of which fall under the AWS Storage Services list.
What is AWS Elastic File System?
From the aforementioned list, EFS falls under the file storage category. EFS is a file-level, fully managed, storage provided by AWS (Amazon Web Services) that can be accessed by multiple EC2 instances concurrently. Just like the AWS EBS, EFS is specially designed for high throughput and low latency applications.
How Does Amazon EFS Work?
Amazon EFS (Elastic File System) is a fully managed, scalable file storage service. You start by creating an EFS from an EC2 instance in a specific region. Then, EFS automatically distributes your data across multiple Availability Zones, ensuring high availability and durability. You can also select the performance mode based on the I/O operations your applications require.
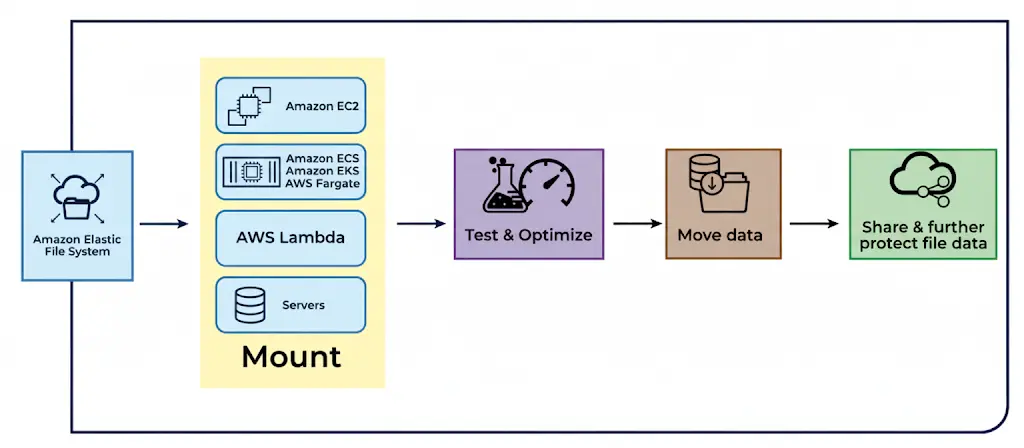
Next, set up mount targets to connect your EFS file system to other AWS resources. EFS allows mounting on several services, such as:
- Amazon EC2
- Amazon ECS
- Amazon EKS
- AWS Fargate
- AWS Lambda
- Other supported servers
With EFS, multiple instances and services can read and write files simultaneously. Therefore, it works perfectly for shared storage in cloud-native applications. Additionally, it scales automatically as your storage needs grow.
Use Cases Of EFS
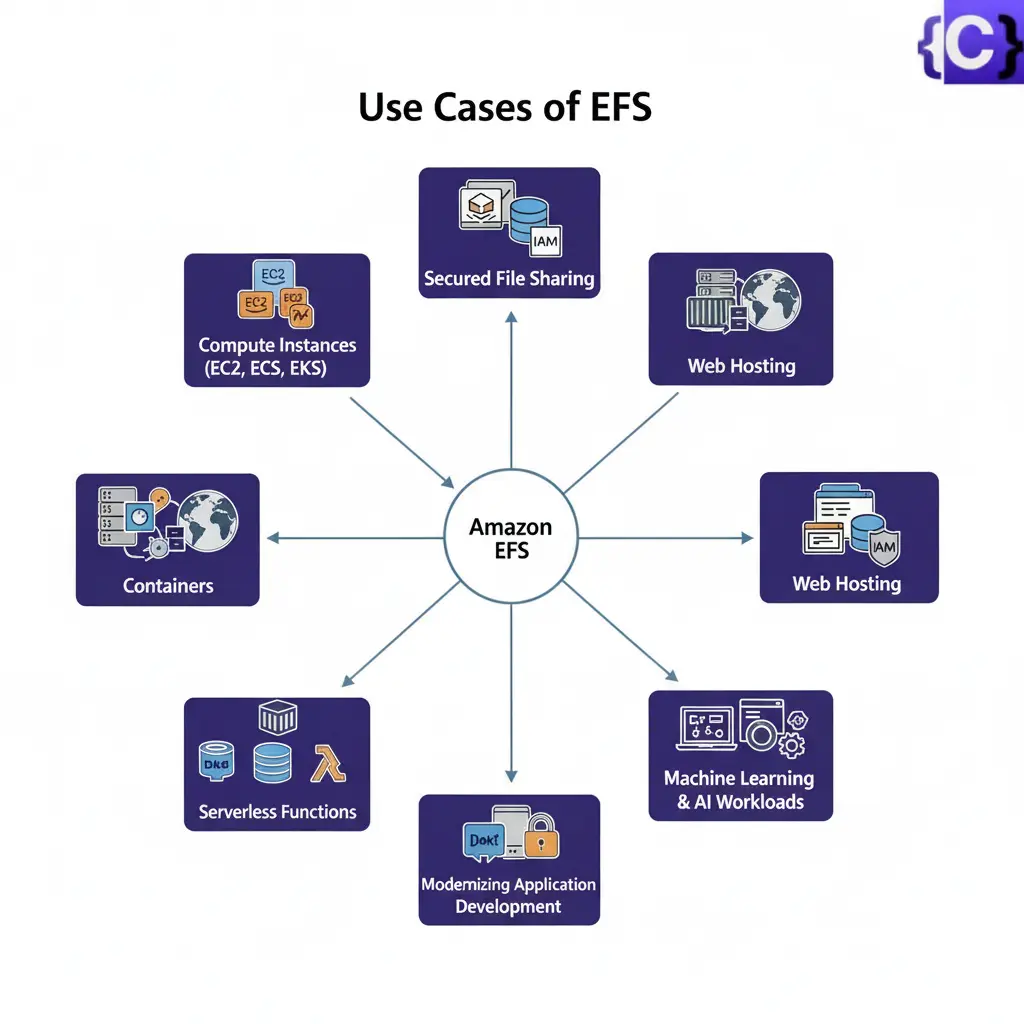
- Secured file sharing: You can share your files in every secured manner and in a faster and easier way and also ensures consistency across the system.
- Web Hosting: Well suited for web servers where multiple web servers can access the file system and can store the data EFS also scales whenever the data incoming is increased.
- Modernize application development: You can share the data from the AWS resources like ECS, EKS, and any serverless web applications in an efficient manner and without more management required.
- Machine Learning and AI Workloads: EFS is well suited for large data AI applications where multiple instances and containers will access the same data improving collaboration and reducing data duplication.
Above are some of the use cases of AWS EFS widely used for handling larger datasets type applications.
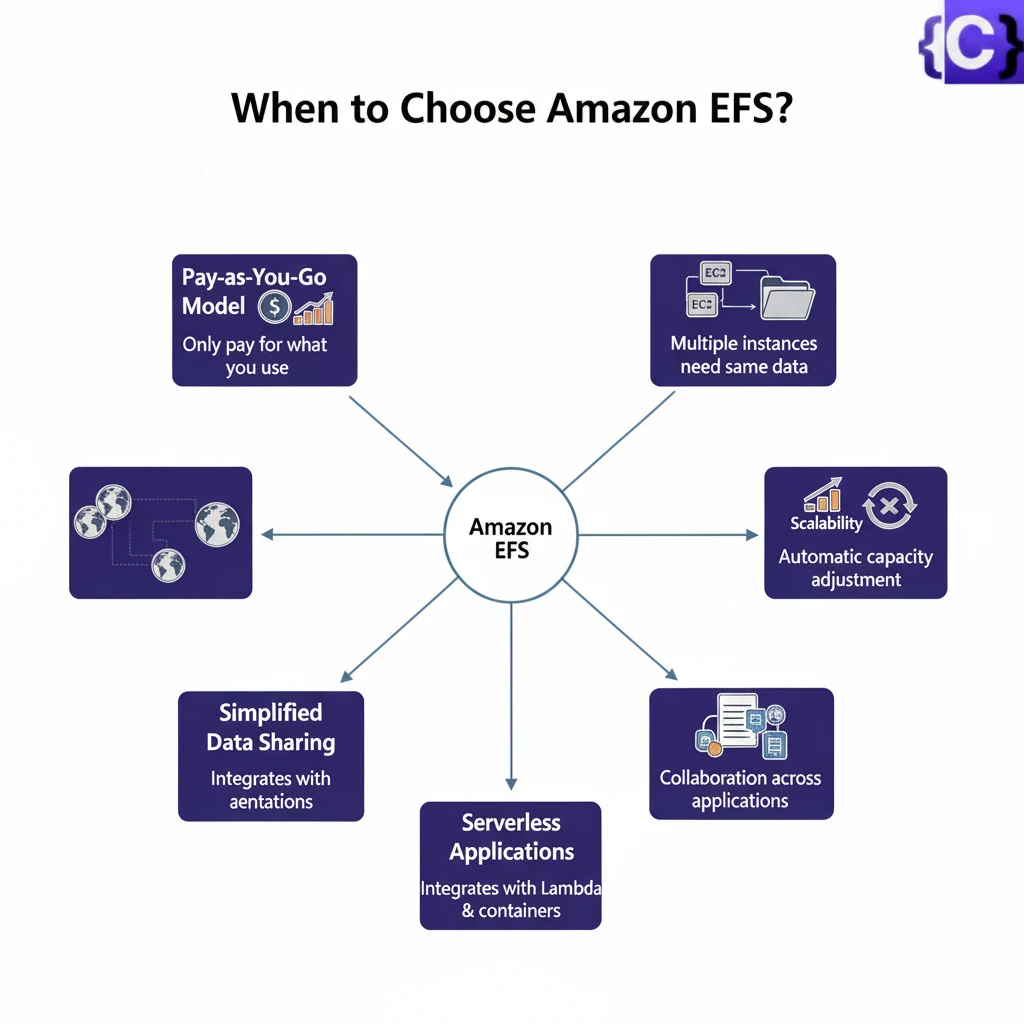
When to Choose Amazon EFS?
Amazon EFS is ideal for several scenarios:
Pay-as-You-Go Model
EFS charges only for the storage you use. You do not need to pay upfront or make long-term commitments, which makes it suitable for applications with unpredictable storage growth
Shared File Storage
Use EFS when multiple EC2 instances need access to the same data. EFS manages shared data and ensures consistency across all instances.
Scalability
EFS automatically adjusts its storage capacity as your data grows or shrinks. If you are unsure how much data will come in, EFS handles it without manual intervention.
Simplified Data Sharing
When different applications require access to the same data for collaboration, EFS works perfectly. It can share large datasets across multiple instances efficiently.
Serverless Applications
Amazon EFS integrates seamlessly with serverless services such as AWS Lambda. It provides reliable storage for serverless workloads.
How is Amazon EFS Different Than Amazon S3?
Amazon EFS (Elastic file system) and S3 (Simple Storage Service) are two different storage services provided by Amazon web services with two different purposes one storage is to store static data and another is to store dynamic data.
| Elastic File System | Simple Storage Service |
|---|---|
| EFS can be accessed by multiple EC2-instance at the same time which can analyze the data and can use the data combined. | S3 is an object storage that is mainly used to store and retrieve static data the data is stored in the form of objects. |
| If any changes are made by one instance to the data it is visible to the other instances immediately. | When you perform the read and write operations on the data you will always get the most updated version of the data only. |
| Widely used for the scenarios like data sharing with multiple instances. | Commonly used for backup, restoring, and hosting static content. |
How is Amazon EFS Different Than Amazon EBS?
Amazon EFS ( Elastic file system) and Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store) are two different services provided by Amazon web services for different use cases.
| Elastic File System | Elastic Block Store |
|---|---|
| If the application is required to share the shared file access then you can choose the Elastic file system. | If the application requires separate storage then you can use the block store. |
| Multiple instances can access the storage system at once. | A single instance only can access the storage system at once. |
| Deliveries the aggregate throughputs to thousands of clients simultaneously. | Highly available with low latency. |
Different Storage Classes in AWS EFS
Standard storage class
- This is the default storage class for EFS.
- The user is only charged for the amount of storage used.
- This is recommended for storing frequently accessed files.
Infrequently Accessed storage class(One Zone)
- Cheaper storage space.
- Recommended for rarely accessed files.
- Increased latency when reading or writing files.
- The user is charged not only for the storage of files but also charged for read and write operations.

Different Performance Modes in EFS
General-purpose
- Offers low latency.
- Supports a maximum of 7000 IOPS.
- As a cloud watch metric, you can view the amount of IOPS your architecture uses and can switch to Max IOPS if required.
Max I/O
- This is recommended when EFS needs over 7000 IOPS
- Theoretically, this mode has an unlimited I/O speed.

Different Throughput Modes in EFS
- Burst Mode: Allows 100MBPS of burst speed per TB of storage.
- Provisioned Mode: Users can decide the max burst speed of the EFS but are charged more when speeds go beyond the default limit.

Steps To Configure and Connect To EFS(Elastic File Storage)
First, create an AWS account create refer to Amazon Web Services – Setting Up an AWS Account.
Step 1: Create an EFS from the AWS console. Choose the correct VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) and configuration that suits your use case.
.webp)
Step 2: Create one or more EC2 servers from the EC2 dashboard as needed for your use case.
Step 3: Allow the EC2 security group to access EFS. Connect To EFS from your EC2 servers. Primarily there are 2 methods of connecting to EFS from EC2 servers: Linux NFS Client: This is the old traditional method of connecting to file systems.EFS Mount Helper: This is the AWS-recommended and simpler solution to connect to EFS.
-(1).webp)
.webp)
- Once you have connected to AWS EFS from your EC2 instances you will have a folder of any name (say EFS-Folder) which will hold all the files in the EFS. Any file created in this directory can be seen or edited from any EC2 instances that have access to the EFS.
Features of AWS EFS
- Storage capacity: Theoretically EFS provides an infinite amount of storage capacity. This capacity grows and shrinks as required by the user.
- Fully Managed: Being an AWS-managed service, EFS takes the overhead of creating, managing, and maintaining file servers and storage.
- Multi EC2- Instance Connectivity: EFS can be shared between any number of EC2- instances by using mount targets.
- Note-: A mount target is an Access point for AWS EFS that is further attached to EC2 instances, allowing then access to the EFS.
- Availability: AWS EFS is region specific., however, can be present in multiple availability zones in a single region.
- EC2- instances across different availability zones can connect to EFS in that zone for a quicker access
- EFS LifeCycle Management: Lifecycle management moved files between storage classes. Users can select a retention period parameter (in number of days). Any file in standard storage which is not accessed for this time period is moved to the Infrequently accessed class for cost-saving.
- Note that the retention period of the file in standard storage resets each time the file is accessed
- Files once accessed in the IA EFS class are then moved to Standard storage.
- Note that file metadata and files under 128KB cannot be transferred to the IA storage class.
- LifeCycle management can be turned on and off as deemed fit by the users.
- Durability: Multi-availability zone presence accounts for the high durability of the Elastic File System.
- Transfer: Data can be transferred from on-premise to the EFS in the cloud using AWS Data Sync Service. Data Sync can also be used to transfer data between multiple EFS across regions.
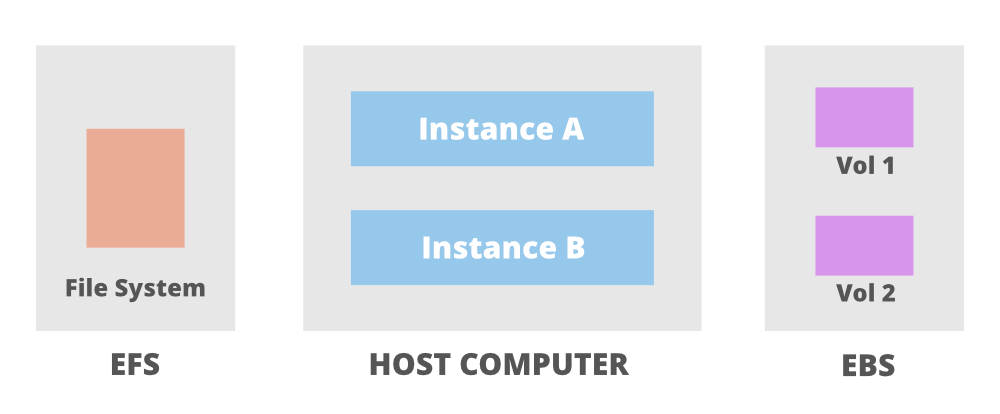
The above image shows an Elastic File System shared between two instances which are further connected to their own EBS volumes.
Advantages of AWS Elastic File System(EFS)
- EFS is scalable and elastic where you can scale the EFS depending on the data that is going to be stored. The scaling is done automatically.
- Multiple instances in AWS can access the EFS simultaneously. It makes it easy to share data across instances.
- Within the same region, the EFS replicates the data to the multiple availability zones.
- EFS allows you to take a backup of data from time to time so if there is any data loss you can always have backup.
- EFS supports a wide range of POSIX file system features, making it compatible with many Linux-based applications
Limitations of AWS Elastic File System(EFS)
There are a few limitations to consider when using AWS Elastic File System (EFS).
- EFS only supports the Network File System (NFS) protocol, so it can only be mounted and accessed by devices that support NFS.
- EFS has a maximum file size of 47.9 TB.
- EFS has a maximum throughput of 1000 MB/s per file system and a maximum of 16,000 IOPS per file system.
- EFS has a maximum number of files and directories that can be created within a single file system, which is determined by the size of the file system. For example, a 1 TB file system can support up to about 20 million files and directories.
- EFS is only available in certain regions, and it is not possible to migrate data between regions.
Conclusion
AWS Elastic File System (EFS) is a highly scalable, fully managed, and elastic file storage service designed to provide shared access across multiple EC2 instances and other AWS services. Its ability to automatically scale storage, replicate data across multiple availability zones, and support POSIX-compliant file systems makes it an ideal choice for applications that require high availability, low latency, and collaborative data access. EFS is especially suited for use cases such as secure file sharing, web hosting, serverless applications, and large-scale AI or machine learning workloads.
While EFS offers many advantages like automatic scaling, lifecycle management, and seamless integration with AWS services, it also has limitations, including NFS-only support, maximum file system throughput and file size constraints, and regional availability restrictions. Despite these limitations, EFS remains a robust and flexible solution for dynamic, shared, and high-performance file storage in the cloud, making it a critical component of modern AWS architectures.


