In cloud computing, managing networks across different components often becomes complex. AWS created Transit Gateway to simplify network design inside the AWS Cloud.
Transit Gateway is a fully managed service. It acts as a central hub that connects multiple virtual private clouds (VPCs) and on-premises networks. The service routes and manages traffic. It delivers a scalable and efficient solution for organizations with varied networking needs.
This article covers key terms, core features, and the benefits of Transit Gateway. It also provides a step-by-step guide to deployment and answers common questions. By the end, you will have a clear understanding of this important AWS service.
Primary Terminologies
AWS Transit Gateway
AWS Transit Gateway is a managed service from Amazon Web Services (AWS). It acts as a central hub that connects multiple VPCs and on-premises networks. By consolidating connectivity and routing, it simplifies network management and helps organizations scale their infrastructure easily.
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
A Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a dedicated virtual network for an AWS account. It provides an isolated section of the AWS Cloud where users can launch resources such as EC2 instances, databases, and Lambda functions. As a result, businesses gain full control over their cloud environment.
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a secure connection between a user’s network and AWS. Organizations often use it to extend on-premises infrastructure into the cloud. Moreover, VPN connections encrypt data traffic, which ensures safe communication over the internet.
Route Tables
Route tables control how network traffic flows inside a VPC or between a VPC and external networks. In the case of AWS Transit Gateway, route tables define destinations for traffic coming from attached VPCs and VPN connections. Therefore, they play a critical role in managing traffic paths.
Attachments
Attachments in AWS Transit Gateway represent the links between the gateway and other resources, such as VPCs or VPNs. These attachments allow traffic to move smoothly between the Transit Gateway and connected resources. Consequently, they enable seamless communication across the network.
What is AWS Transit Gateway?
AWS Transit Gateway is a completely managed service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that improves network performance in the cloud by acting as a unified center point for associating various virtual private clouds (VPCs) and on-premises networks. It permits associations to unite their organizational architecture, streamline routing, and manage networks all the more effectively.
Key features of AWS Transit Gateway
Centralized Hub: AWS Transit Gateway fills in as a main issue for connecting numerous VPCs, VPN connections, and on-premises networks. This hub and-spoke architecture works on network the executives by giving a single gateway to routing traffic between different network resources.
Scalability: AWS Transit Gateway is exceptionally adaptable and can uphold huge number of VPCs and VPN associations inside a single AWS account. It takes out the need to oversee complex peering connections between VPCs, allowing associations to consistently scale their network infrastructure.
Transitive Routing: Transit Gateway supports transitive routing, empowering traffic to flow between joined VPCs and VPN connections without the requirement for complex routing configurations. This improves on availability between various network segments and upgrades network agility.
Why Use AWS Transit Gateway?
- Centralized Connectivity – Connect multiple VPCs and
on-premises environments efficiently. - Scalability – Supports thousands of connections without
the complexity of managing individual peering links. - Simplified Routing – Reduces the need for complex route
tables and simplifies traffic flow between networks. - Multi-Account & Multi-Region Support – Easily link
VPCs across AWS Organizations and different AWS
regions. - High-Performance & Cost-Efficient – Optimized for lowlatency and cost-effective inter-VPC communication.
Common Use Cases of AWS Transit Gateway
- Connect Multiple VPCs: AWS Transit Gateway allows you to link multiple VPCs in a hub-and-spoke architecture, simplifying network management.
- Hybrid Cloud Networks: You can integrate on-premises data centers with AWS, creating a seamless hybrid cloud environment.
- Centralized Security Monitoring: Transit Gateway enables centralized monitoring of traffic across different networks and environments.
- Disaster Recovery and Workload Migration: It supports multi-region disaster recovery and migration of workloads between networks.
- Cross-Network Communication: Multiple VPCs can communicate with each other—even if they belong to different cloud providers like AWS or Azure, or exist in on-premises networks—without using the public internet.
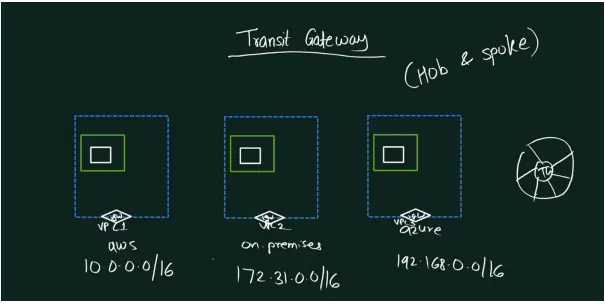
Example Scenario
In the diagram, three instances exist in three separate VPCs. Two of them are hosted by different cloud providers, and one is on-premises. Using Transit Gateway, these instances can communicate directly through their private IPs. This eliminates the need for public internet access, ensuring secure and efficient communication.
Step-by-Step Process to Create AWS Transit Gateway
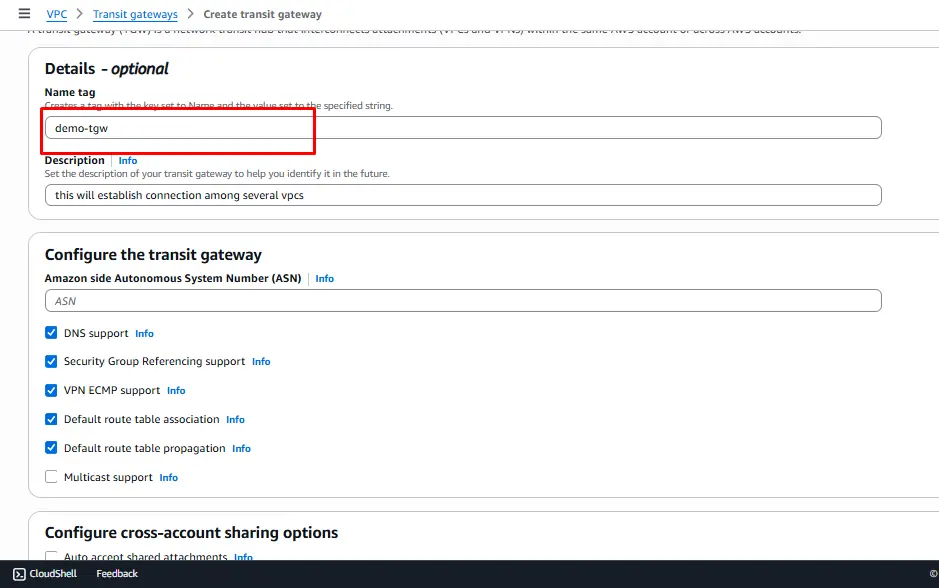
Step 1: Create Transit Gateway
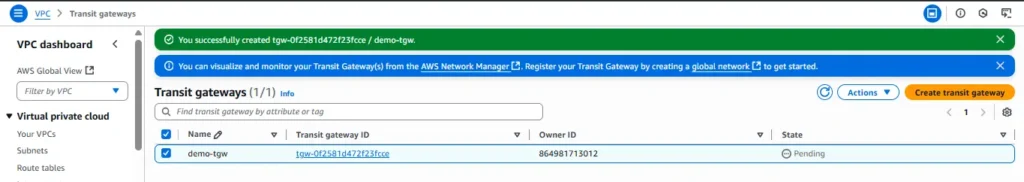
A transit gateway (TGW) is a network transit hub that interconnects attachments (VPCs and VPNs) within the same AWS account or across AWS accounts. Navigate to Transit Gateway and click on Create transit gateways
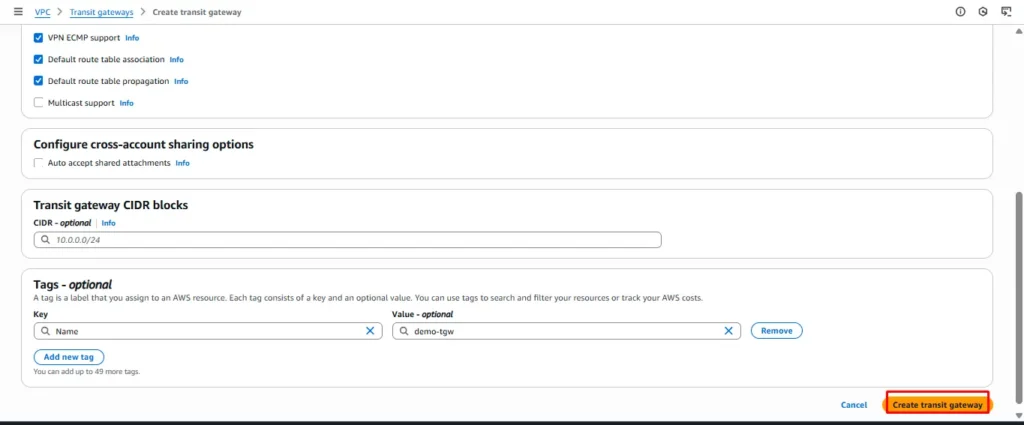
Now click on create Transit Gateway
Here we see transit gateway successfully created
Step 2: Configuring VPCs
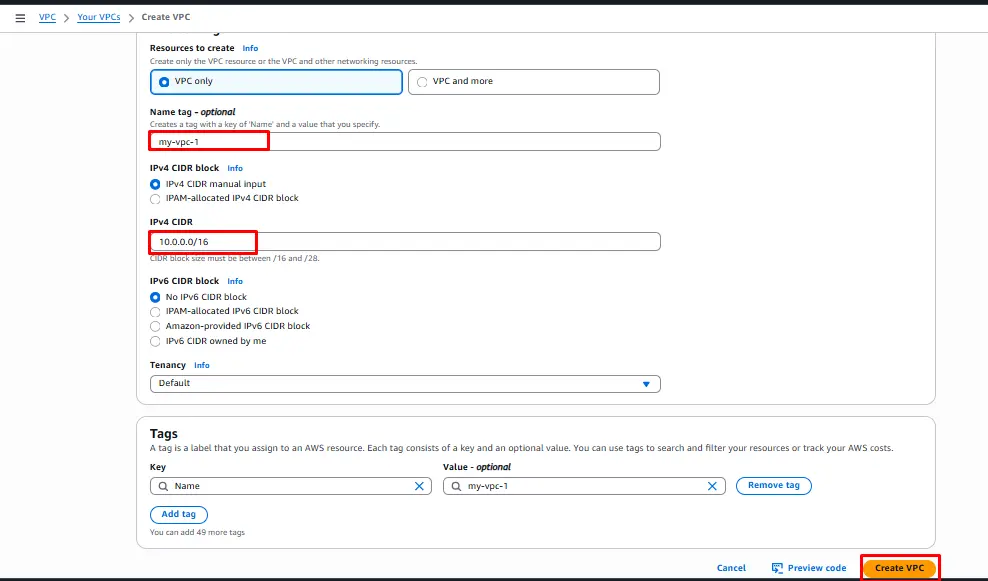
Navigate to VPC Dashboard and click on create VPC.
A VPC is an isolated portion of the AWS Cloud populated by AWS objects, such as Amazon EC2 instances.
Now create two VPCs or select existing VPCs.
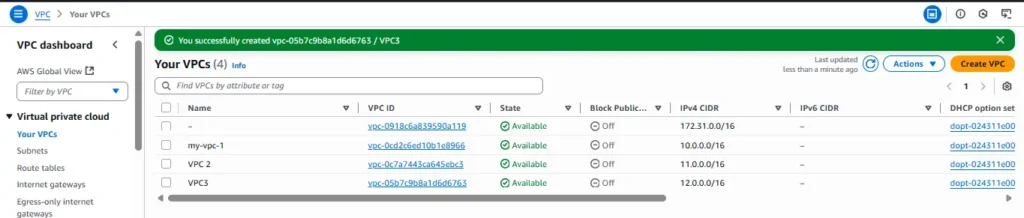
Same process do for VPC2 and VPC3 ,Here we see two VPC are created.
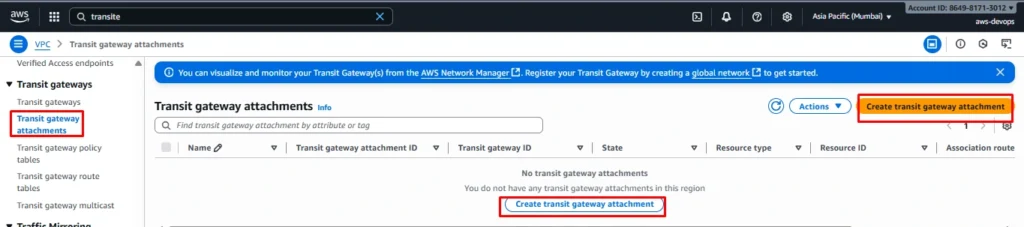
Step 3: Transit Gateway Attachments
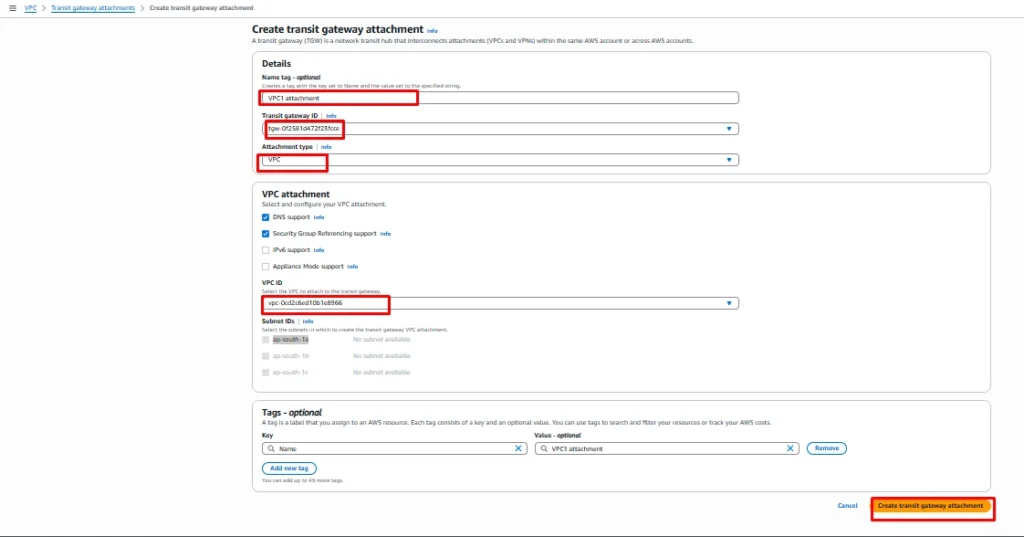
Now select Transit gateway ID which is created in previous step and next select attachment type VPC or VPN.
VPC attachment: Select and configure your VPC attachment.
VPC ID: Select the VPC1 to attach to the transit gateway.
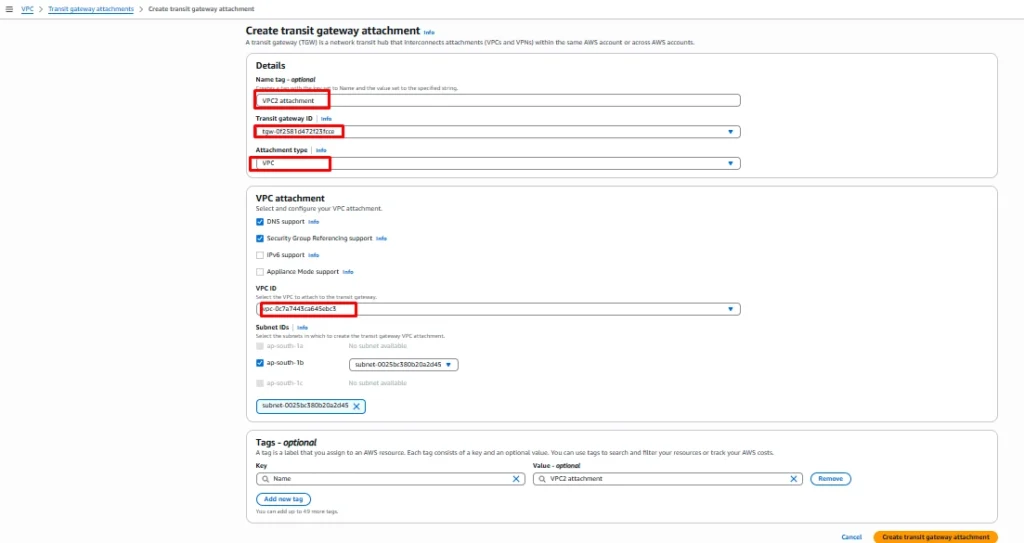
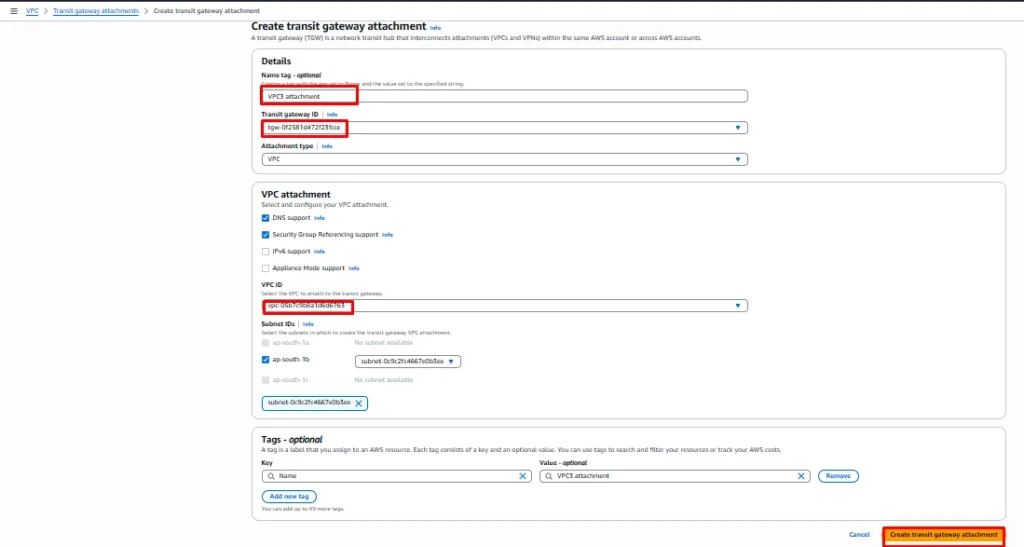
Same we need to do on VPC2 and VPC3 as well.
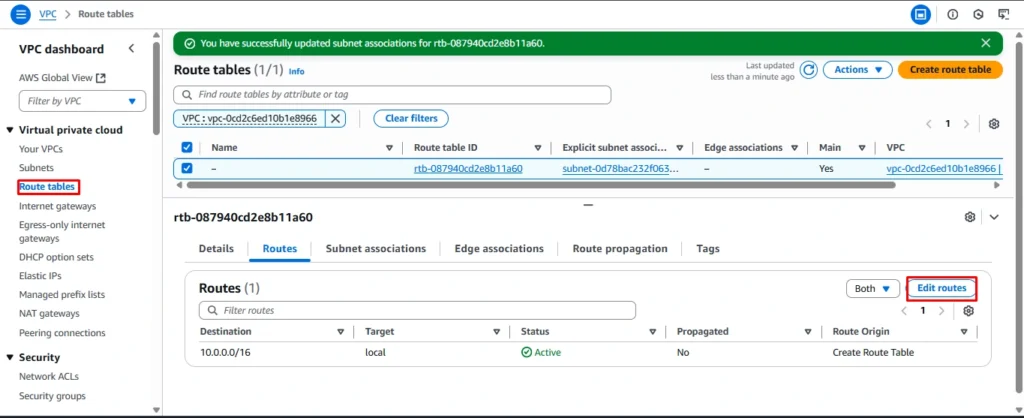
Step 4: Creating route Tables
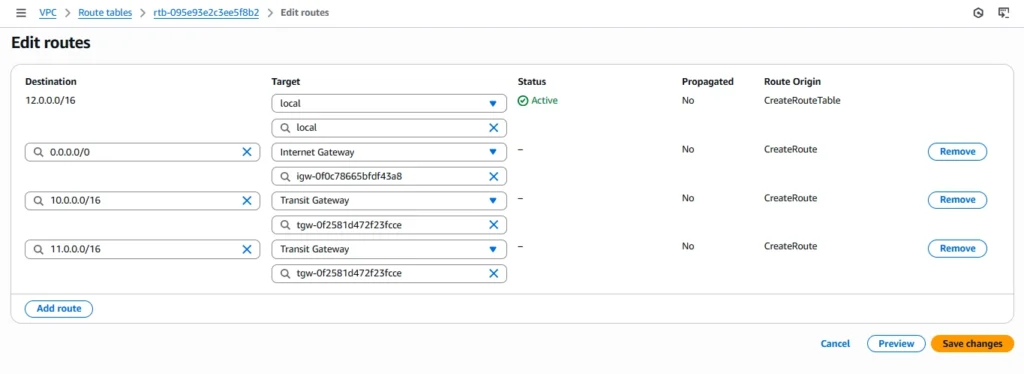
Click on Edit route and choose add route
In previous step we are created VPC along with Route Table, Now we need to attach our Transit gateway to route table
Now choose Private route table and navigate to routes
Set cidr block for vpc 2 and vpc3 and in drop down box select Transit gateway and click save changes
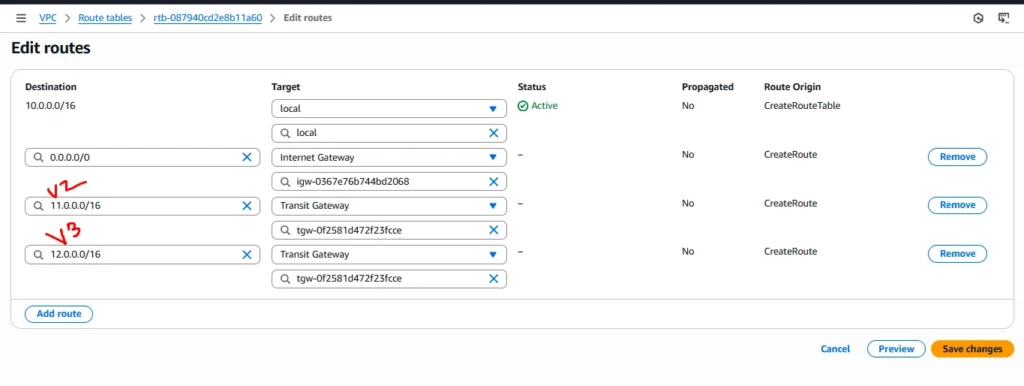
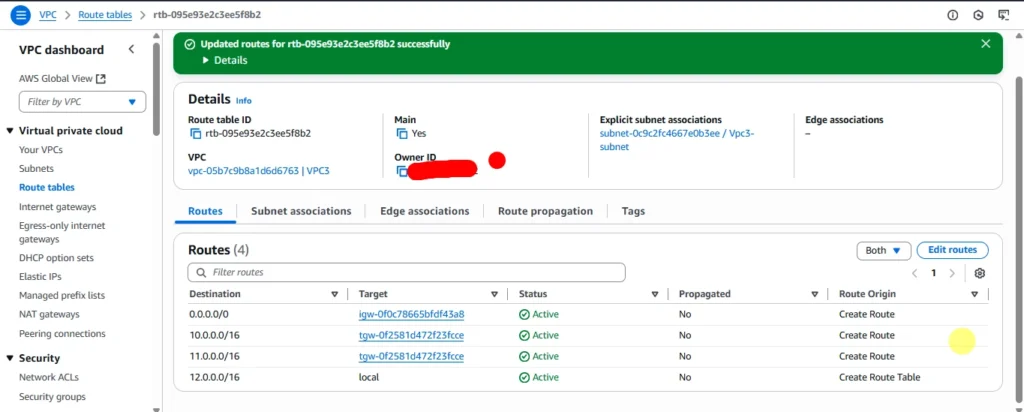
Route table was updated
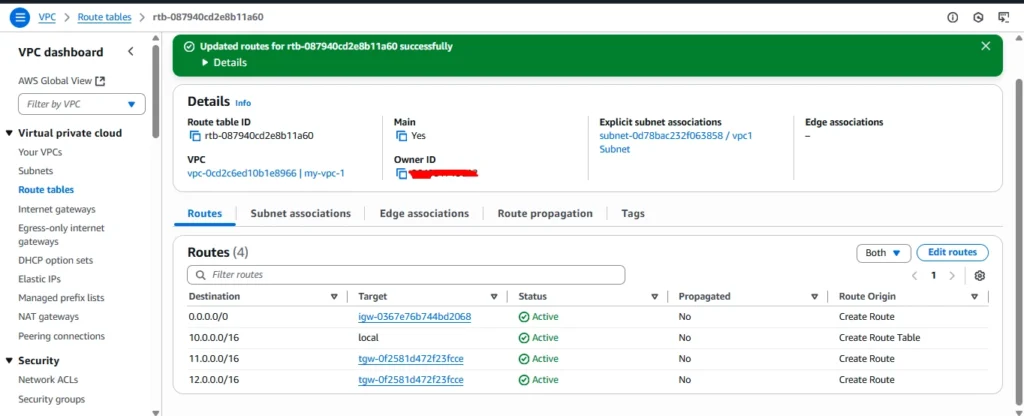
Now same process we need to do for the VPC2 and VPC3 as well.
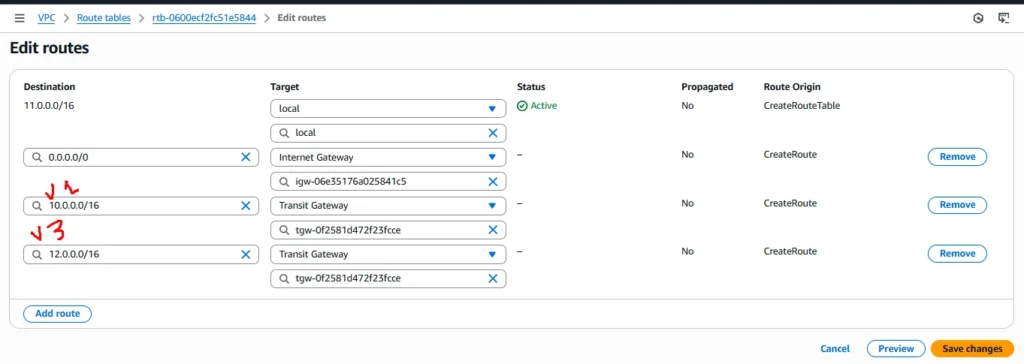
Route table for vpc3
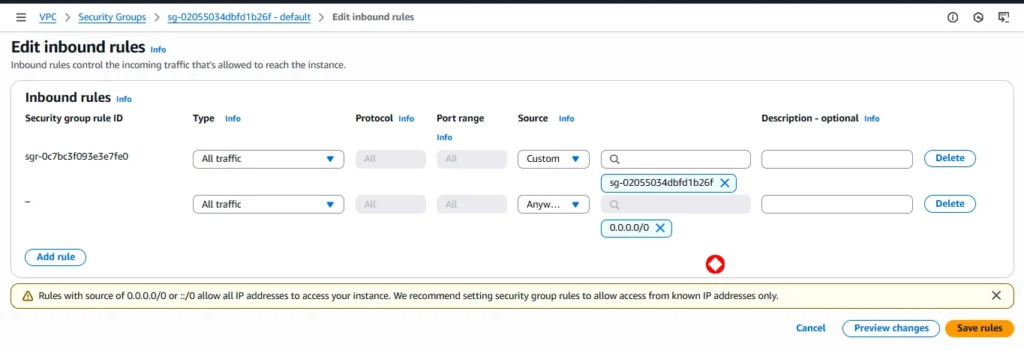
Step 5: Configuring security groups
Now edit inbound rules to security groups allow all traffic for testing purpose
Create New Security Groups or select existing security group
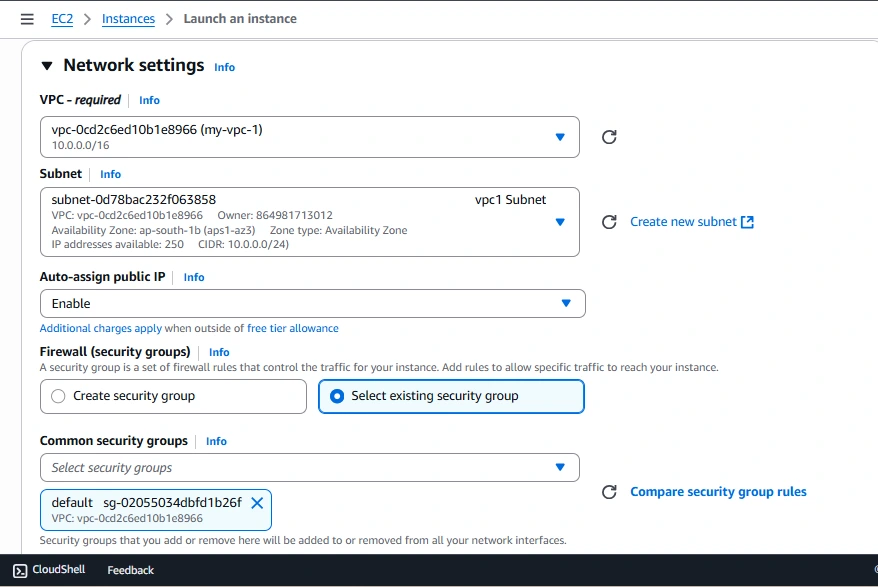
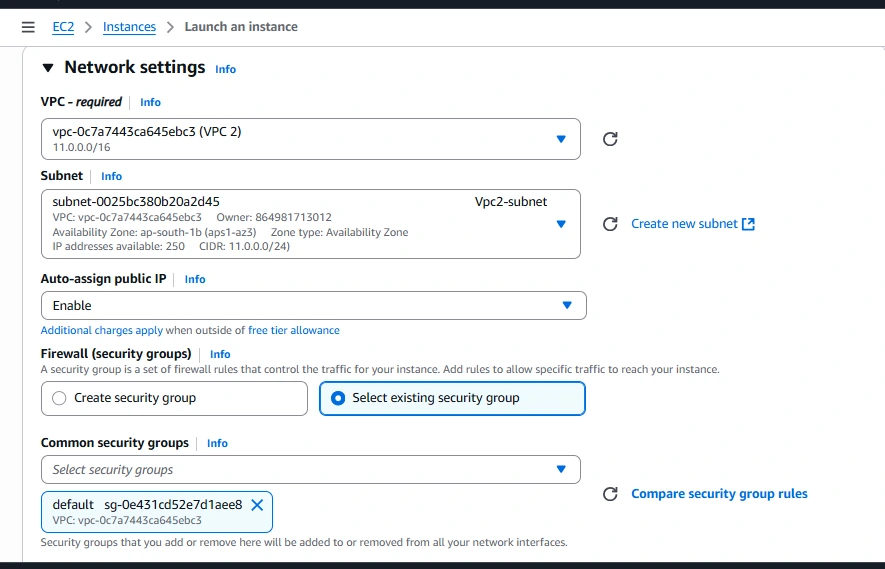
Step 6: Launch EC2 Instance
While launching instances in network settings choose created VPCs and also choose public subnet as shown in below figure
Instance-1
Launce the instance from the vpc one with the public subnet, SSH into a EC2 Host and copy the key pair (.pem file) to an EC2 instance in VPC1.
Instance-2
Launce the instance from the vpc two with the public subnet
Here is the command to be execute in terminal
ssh -i /path/to/your/keypair.pem ec2-user@public-ip
Output
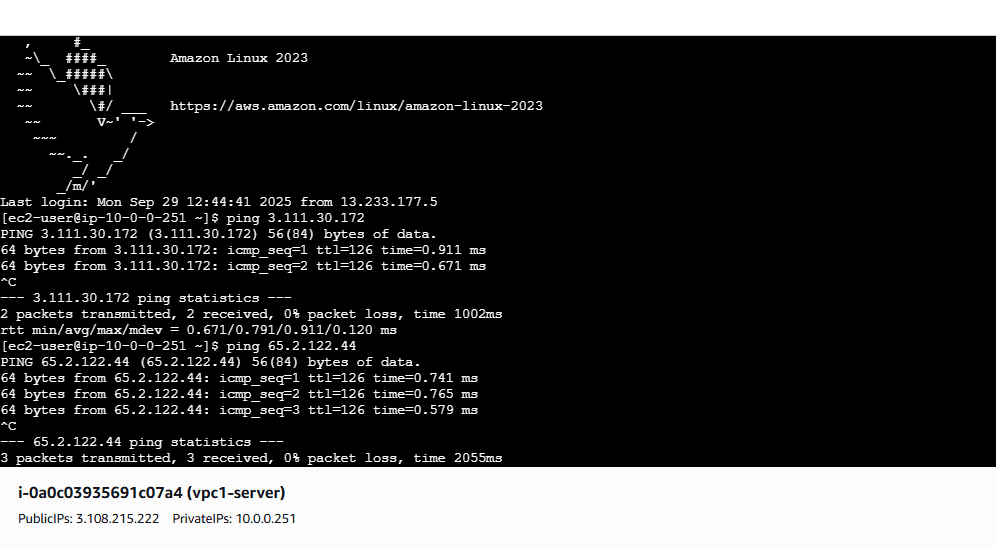
Here we see VPC 1 to VPC 2 and VPC3
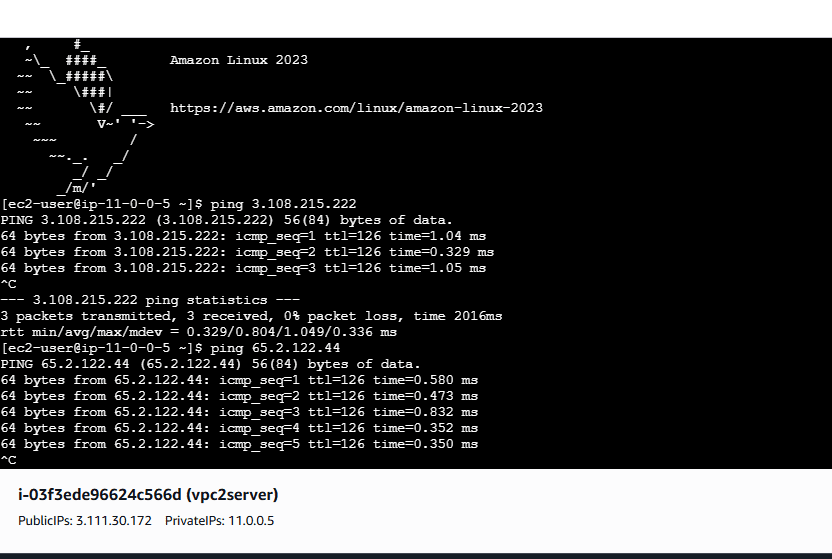
Here we see VPC 2 to VPC 1 and VPC3
AWS Transit Gateway Pricing
AWS Transit Gateway pricing depends on two main components: the number of attachments and the amount of data transferred through the gateway. Below is a detailed breakdown to help you understand potential costs.
| Component | Description | Pricing (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Transit Gateway Attachment | Cost for each VPC, VPN, or Direct Connect attachment connected to the Transit Gateway. | $0.05 per attachment per hour |
| Data Processing | Cost for processing data that traverses the Transit Gateway. | $0.02 per GB |
| Inter-Region Data Transfer | Cost for transferring data between VPCs in different AWS regions via the Transit Gateway. | $0.02 per GB |
| VPN Attachment | Cost for attaching a VPN connection to the Transit Gateway. | $0.05 per VPN attachment per hour |
| Direct Connect Gateway Attachment | Cost for linking a Direct Connect gateway to the Transit Gateway. | $0.05 per attachment per hour |
| Transit Gateway Peering | For peering connections between Transit Gateways in different regions. | $0.01 per GB data transfer between TGWs |
| Optional Features | Features like multicast support, traffic mirroring, and AWS PrivateLink may have additional costs. | Varies based on usage |
Conclusion
AWS Transit Gateway reforms cloud network availability by filling in as a centralized hub for connecting different VPCs and on-premises networks. With worked on administration and transitive routing capacities, it smoothest out network architecture, improves versatility, and advances consistent correspondence between resources. This versatile arrangement obliges great many associations, ensuring adaptability for advancing cloud conditions. By integrating consistently with AWS services, Transit Gateway augments functional effectiveness and works with light-footed network deployments, its inter region looking element empowers global network, engaging associations to construct strong, geographically distributed architectures.